166 State of Palestine

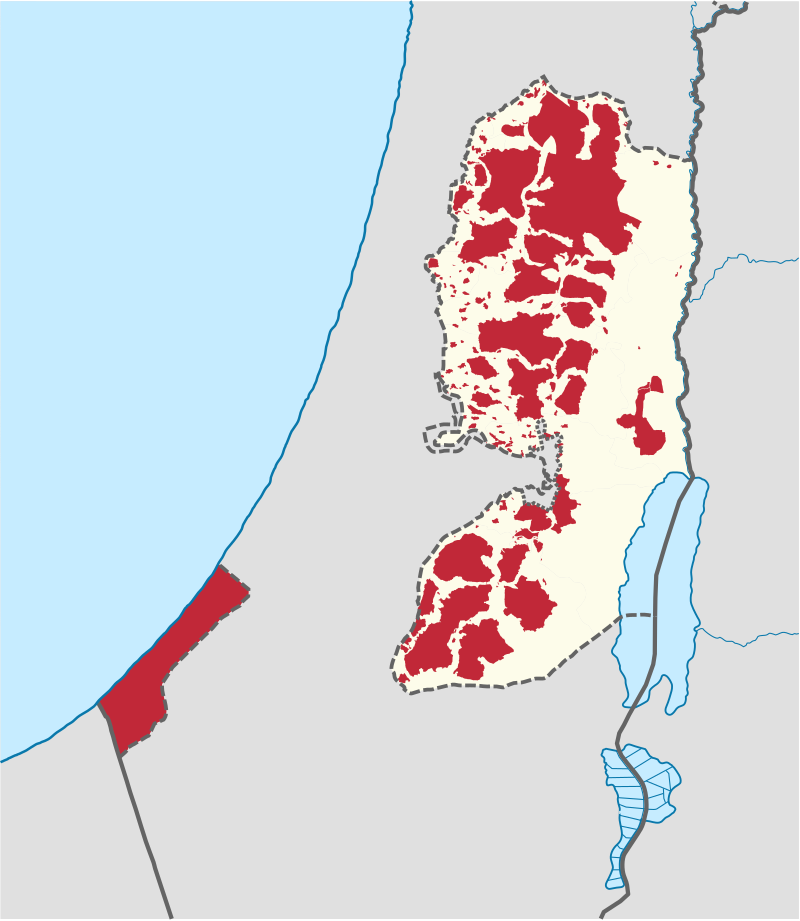
Map of the Palestinian Authority showing the Palestinian enclaves currently under Palestinian administration in red (Areas A and B; not including Gaza Strip, which is under Hamas rule)

Children waving a Palestinian flag, West Bank
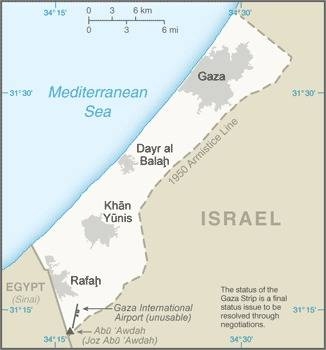
Map of the Gaza Strip courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Last updated on March 23, 2025
Government
According to Britannica, if one chief theme in the post-1948 pattern was embattled Israel and a second the hostility of its Arab neighbors, a third was the plight of the huge number of Arab refugees. The violent birth of Israel led to a major displacement of the Arab population, who either were driven out by Zionist military forces before May 15, 1948, or by the Israeli army after that date or fled for fear of violence by these forces. Many wealthy merchants and leading urban notables from Jaffa, Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Jerusalem fled to Lebanon, Egypt, and Jordan, while the middle class tended to move to all-Arab towns such as Nāblus and Nazareth. The majority of fellahin ended up in refugee camps. More than 400 Arab villages disappeared, and Arab life in the coastal cities (especially Jaffa and Haifa) virtually disintegrated. The centre of Palestinian life shifted to the Arab towns of the hilly eastern portion of the region, which was immediately west of the Jordan River and came to be called the West Bank.
Like everything else in the Arab-Israeli conflict, population figures are hotly disputed. Nearly 1,400,000 Arabs lived in Palestine when the war broke out. Estimates of the number of Arabs displaced from their original homes, villages, and neighborhoods during the period from December 1947 to January 1949 range from about 520,000 to about 1,000,000; there is general consensus, however, that the actual number was more than 600,000 and likely exceeded 700,000. Some 276,000 moved to the West Bank; by 1949 more than half the prewar Arab population of Palestine lived in the West Bank (from 400,000 in 1947 to more than 700,000). Between 160,000 and 190,000 fled to the Gaza Strip. More than one-fifth of Palestinian Arabs left Palestine altogether. About 100,000 of these went to Lebanon, 100,000 to Jordan, between 75,000 and 90,000 to Syria, 7,000 to 10,000 to Egypt, and 4,000 to Iraq.
Henceforth the term Palestinian will be used when referring to the Arabs of the former mandated Palestine, excluding Israel. Although the Arabs of Palestine had been creating and developing a Palestinian identity for about 200 years, the idea that Palestinians form a distinct people is relatively recent. The Arabs living in Palestine had never had a separate state. Until the establishment of Israel, the term Palestinian was used by Jews and foreigners to describe the inhabitants of Palestine and had only begun to be used by the Arabs themselves at the turn of the 20th century. With the Arab world in a period of renaissance popularizing notions of Arab unity and nationalism amid the decline of the Ottoman Empire, most saw themselves as part of the larger Arab or Muslim community. The Arabs of Palestine began widely using the term Palestinian starting in the pre-World War I period to indicate the nationalist concept of a Palestinian people. But after 1948, and even more so after 1967, for Palestinians themselves the term came to signify not only a place of origin but, more importantly, a sense of a shared past and future in the form of a Palestinian state.
Approximately 150,000 Arabs remained in Israel when the Israeli state was founded. This group represented about one-eighth of all Palestinians and by 1952 roughly the same proportion of the Israeli population. The majority of them lived in villages in western Galilee. Because much of their land was confiscated, Arabs were forced to abandon agriculture and become unskilled wage laborers, working in Jewish industries and construction companies. As citizens of the State of Israel, in theory they were guaranteed equal religious and civil rights with Jews. In reality, however, until 1966 they lived under a military jurisdiction that imposed severe restrictions on their political options and freedom of movement. Most of them remained politically quiescent, and many acquiesced to the reality of an Israel governed according to the ideology of Zionism. Many also sought to ameliorate their circumstances through electoral participation, education, and economic integration.
Israel sought to impede the development of a cohesive national consciousness among the Palestinians by dealing with various minority groups, such as Druze, Circassians, and Bedouin; by hindering the work of the Muslim religious organizations; by arresting and harassing individuals suspected of harboring nationalist sentiments; and by focusing on education as a means of creating a new Israeli Arab identity. By the late 1960s, as agriculture declined and social customs related to such events as bride selection and marriage broke down, the old patriarchal clan system had all but collapsed. For almost 20 years after Israel was established, Palestinian citizens of Israel were isolated from other Arabs.
The Jordanian monarchy saw in the events of 1948–49 the opportunity to expand Jordanian territory and to integrate Palestinians into its population and thereby create a new inclusive Jordanian nationality. Through a series of political and social policies, Jordan sought to consolidate its control over the political future of Palestinians and to become their speaker. It provided education and, in 1949, extended citizenship to Palestinians; indeed, a majority of all Palestinians became Jordanian citizens. However, tensions soon developed between original Jordanian citizens and the better-educated, more skilled newcomers. Wealthy Palestinians lived in the towns of the eastern and western sides of the Jordan River, competing for positions within the government, while the fellahin filled the UN refugee camps.
Palestinians constituted about two-thirds of the population of Jordan. Half the seats in the Jordanian Chamber of Deputies were reserved for representatives from the West Bank, but this measure and similar attempts to integrate the West Bank with the area lying east of the Jordan River were made difficult by the significant social, economic, educational, and political differences between the residents of each. Jordanian Palestinians, other than the notable families favored by the Jordanian monarchy, tended to support the radical pan-Arab and anti-Israeli policies of Egypt’s President Gamal Abdel Nasser rather than the more cautious and conciliatory position of Jordan’s King Ḥussein.
During the 20 years the Gaza Strip was under Egyptian control (1948–67), it remained little more than a reservation. Egyptian rule was generally repressive. Palestinians living in the region were denied citizenship, which rendered them stateless (i.e., it left them without citizenship of any nation), and they were allowed little real control over local administration. They were, however, allowed to attend Egyptian universities and, at times, to elect local officials.
In 1948 Amīn al-Ḥusaynī declared a Government of All Palestine in the Gaza Strip. However, because it was totally dependent on Egypt, it was short-lived. The failure of this venture and al-Ḥusaynī’s lack of credibility because of his collaboration with the Axis powers during World War II did much to weaken Palestinian Arab nationalism in the 1950s.
The Gaza Strip, 25 miles (40 km) long and 4–5 miles (6–8 km) wide, became one of the most densely populated areas of the world, with more than four-fifths of its population urban. Poverty and social misery became characteristic of life in the region. The rate of unemployment was high; many of the Palestinians lived in refugee camps, depending primarily on UN aid. Most of the agricultural lands they had formerly worked were now inaccessible, and little or no industry was allowed, but commerce flourished as Gaza became a kind of duty-free port for Egyptians. Although some Gaza Strip Palestinians were able to leave the territory and gain an education and find employment elsewhere, most had no alternative but to stay in the area, despite its lack of natural resources and jobs.
In December 1949 the UN General Assembly created the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) to assist the Palestinian refugees. In May 1950 UNRWA established a total of 53 refugee “camps” on both sides of the Jordan River and in the Gaza Strip, Lebanon, and Syria to assist the 650,000 or more Arab refugees it calculated needed help. Initially refugees in the improvised camps lived in tents, but after 1958 these were replaced by small houses of concrete blocks with iron roofs. Conditions were extremely harsh; often several families had to share one tent, and exposure to the extreme winter and summer temperatures inflicted additional suffering. Loss of home and income lowered morale. Although the refugees were provided with rent-free accommodations and basic services such as water, health care, and education (UNRWA ran both elementary and secondary schools in the camps, teaching more than 40,000 students by 1951), poverty and misery were widespread. Work was scarce, even though UNRWA sought to integrate the Palestinians into the depressed economies of the “host” countries.
Palestinians who continued to live in refugee camps felt a greater sense of alienation and dislocation than the more fortunate ones who found jobs and housing and became integrated into the national economies of the countries in which they resided. Although the camps strengthened family and village ties, their demoralized inhabitants were isolated from mainstream Palestinian political activities during the 1950s.
Palestinians found employment in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, and the Persian Gulf states, but only a few were able to become citizens of those countries. Often they were the victims of discrimination, as well as being closely supervised by the respective governments intent on limiting their political activities.
The events of 1948 (also called by Palestinians al-nakbah, “the catastrophe”) and the experience of exile shaped Palestinian political and cultural activity for the next generation. The central task of reconstruction fell to Palestinians living outside Israel—both in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip communities and in the new Palestinian communities outside the former British mandate. (Palestinians living within the State of Israel remained in an ambiguous isolated situation and were regarded with some suspicion by both Israelis and other Palestinians.) The new leaders came disproportionately from among those who had moved to various Middle Eastern states and to the West, even though four out of five Palestinians had remained within the borders of the former British mandate. By the mid-1960s, despite Israeli efforts to forestall the emergence of a renewed Palestinian identity, a young educated leadership had arisen, replacing the discredited traditional local and clan leaders.
Palestinian refugee camps differed depending on the country in which they were located, but they shared one common development, the emergence of a “diaspora consciousness.” In time this consciousness grew into a renewed national identity and reinvigorated social institutions, leading to the establishment of more complex social and political structures by the 1960s. A new Palestinian leadership emerged from the schools UNRWA had established, as well as from the universities of Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, western Europe, and the United States. Palestinians living in the UNRWA-administered refugee camps felt isolated, politically powerless, disoriented, bitter, and resentful. They remained unassimilated and were generating a new sense of identity based on a pan-Arabism inspired by Nasser, the cultivated memory of a lost paradise (Palestine), and an emerging pan-Islamic movement.
By the late 1960s a class of educated and mobile Palestinians had emerged, with fewer than half of them living in the West Bank or Gaza. They were working in the oil companies, civil services, and educational institutions of most Arab states in the Middle East. Having successfully resisted the efforts of Amīn al-Ḥusaynī, Jordan, and Egypt to control and speak for them, they joined the process of reshaping Palestinian consciousness and institutions. Thus Palestinians entered a new stage of the struggle for nationhood.
An Arab summit meeting in Cairo in 1964 led to the formation of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). A political umbrella organization of several Palestinian groups, the PLO thereafter consistently claimed to be the sole representative of all Palestinian people. Its first leader was Aḥmad Shuqayrī, a protégé of Egypt. In its 1968 charter (the Palestine National Charter, or Covenant) the PLO delineated its basic principles and goals, the most important of which were the right to an independent state, the total liberation of Palestine, and the destruction of the State of Israel.
A Palestine National Council (PNC) was established to serve as the supreme body, or parliament, of the PLO, and an executive committee was formed to manage PLO activities. Initially, the PNC consisted of civilian representatives from various areas, including Jordan, the West Bank, and the Persian Gulf states, but representatives of guerrilla organizations were added in 1968.
Several years before the creation of the PLO, a secret organization had been formed: the Palestine National Liberation Movement (Ḥarakat al-Taḥrīr al-Waṭanī al-Filasṭīnī), known from a reversal of its Arabic initials as Fatah. Both the PLO and Fatah undertook the training of guerrilla units for raids on Israel. In addition to Fatah, the largest and most influential guerrilla organization, several others emerged in the late 1960s. The most important ones were the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (DFLP), the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine–General Command (PFLP–GC, a splinter group from the PFLP), and al-Ṣāʿiqah (backed by Syria). These groups joined forces inside the PLO despite their differences in ideology and tactics (some were dedicated to openly terrorist tactics). In 1969 Yasser Arafat, leader of Fatah, became chairman of the PLO’s executive committee and thus the chief of the Palestinian national movement.
Despite their differences in tactics and ideology, the guerrilla organizations were united in rejecting any political settlement that did not include what they characterized as the total liberation of Palestine and the return of the refugees to their homeland, goals that were to be achieved through armed struggle. Palestinian spokesmen claimed, however, that, while they aimed at dismantling Israel and purging Palestine of Zionism, they also sought to establish a nonsectarian state in which Jews, Christians, and Muslims could live in equality. Most Israelis doubted the sincerity or practicality of this goal and viewed the PLO as a terrorist organization committed to destroying not only the Zionist state but Israeli Jews.
In the Arab-Israeli war of 1967 (also known as the Six-Day War), Israel defeated the combined forces of Egypt, Syria, and Jordan and also overran large tracts of territory, including East Jerusalem, the West Bank (known to Israelis by the biblical names Judaea and Samaria), and the Gaza Strip. Israel’s victory gave rise to another exodus of Palestinians, with more than 250,000 people fleeing to the eastern bank of the Jordan River. However, roughly 600,000 Palestinians remained in the West Bank and 300,000 in the Gaza Strip. Thus, the 3,000,000 Israeli Jews came to rule some 1,200,000 Arabs (including the 300,000 already living in the State of Israel). Moreover, a movement developed among Israelis who advocated settling the occupied territories, particularly the West Bank, as part of the Jewish patrimony in the Holy Land. Several thousand Israeli Jews settled in the territories in the decade following the war.
In the years following the 1967 war, circumstances changed dramatically for Palestinian citizens of Israel. As a result of their resumed contact with the Palestinians of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, they began to recover from their long period of inactivity. Following the Yom Kippur War of 1973, Palestinians in Israel played a greater role in Israeli institutions. They also were significantly affected by Israel’s economic prosperity, and by the 1980s the economy of Palestinian areas had gained some autonomy, as Palestinians moved from unskilled work to business ownership.
Throughout the 1970s and ’80s the PLO, dominated by Fatah, acted as a state in the making and launched frequent military attacks on Israel. The strategy of armed struggle had been inaugurated as early as the 1950s, and, indeed, guerrilla raids against military and civilian targets in Israel had been a factor leading to the Suez Crisis of 1956 and the 1967 war. However, after 1967 Fatah launched a new wave of violent activities, and the Palestinian guerrilla groups, under the umbrella of the PLO, emerged as an element of major importance in the Middle East. The Arab-Israeli war had discredited Nasser’s Pan-Arabism, and Fatah quickly permeated and mobilized the reunited Palestinian population, providing social services and organizations. One result was an escalating cycle of raids and reprisals between the Palestinian guerrillas and Israel; guerrilla attacks on Israeli occupation forces and terror attacks on Israeli civilians (defended by the PLO until renounced by Arafat in 1988) became a key element in the struggle against Israel.
Although generally recognized as the symbol of the Palestinian national movement, the PLO lacked organizational cohesion. It championed Palestinian distinctiveness and autonomy, but circumstances forced the leadership to remain somewhat distant from the lives of Palestinians. This made it difficult to impose a unified policy. A major problem for the PLO was gaining autonomy in order to pursue Palestinian interests, especially since the effort to do so inevitably brought the organization into conflict with the Arab states in which Palestinians lived.
Within Jordan an understanding was reached whereby the royal government allowed the Palestinian guerrillas independent control of their own bases in the Jordan Valley, but relations between the government and the guerrillas remained uneasy. The guerrillas suspected King Ḥussein, who had to face the damage inflicted upon his country by Israeli reprisals, of preparing to reach a direct settlement with Israel at their expense.
Tensions between the Jordanian army loyal to King Ḥussein and the Palestinian guerrillas erupted in a brief but bloody civil war in September 1970 that became known as “Black September.” On September 6–9 the PFLP hijacked to a Jordanian airstrip three airliners (American, Swiss, and British) with a total of more than 300 people aboard. The hijackers threatened to destroy the aircraft, with the passengers aboard, unless Palestinian guerrillas detained in Europe and Israel were released. All the passengers were freed by September 30, when the PFLP secured its main demands (after destroying the airliners). Full warfare ensued when the Jordanian army moved against the guerrillas.
By September 17 the army was fighting the guerrillas in Amman and in northern Jordan, where the guerrillas were reinforced by Syria-based armored units of the Palestine Liberation Army—a body ostensibly part of the PLO but in fact controlled by Syria. Hostilities formally ended on September 25, with the guerrillas still in control of their northern strongholds. Total casualties were variously estimated at 1,000 to 5,000 people killed and up to 10,000 injured. In 1971, however, the fighting resumed, and the Jordanian army established full control over the whole country and crushed the Palestinian military. From that point on, the king and the PLO were deeply suspicious of each other, and the majority of Palestinians holding Jordanian citizenship, especially those living on the West Bank under Israeli control, became highly critical of the king and his policies.
Driven from Jordan, the PLO intensified its activities in Lebanon. The presence of more than 235,000 Palestinians was a source of tension and conflict in Lebanon, as it had been in Jordan. Palestinians had few rights, and most worked for low wages in poor conditions. Palestinian guerrillas continued to carry out attacks against Israel. Israel countered with raids, primarily into southern Lebanon. The Lebanese government sought to restrict the activities of the Palestinian guerrillas, which led to sporadic fighting between the Lebanese army and the guerrillas.
In 1973 the Palestinian movement suffered a severe blow from an Israeli commando attack in Beirut in April that killed three of its leaders. Following the attack, the Lebanese army assaulted guerrilla bases and refugee camps throughout the country. An agreement was reached requiring the Palestinians to limit their activities to border areas near Israel and refugee camps near urban centers. After 1973 many Palestinians from Lebanon and Jordan moved to the increasingly prosperous and labour-hungry Arab oil states, such as Kuwait and Saudi Arabia.
The PLO made important gains in its international relations during the 1970s. By the end of the decade the organization had representatives in more than 80 countries. On September 22, 1974, the UN General Assembly, overriding strong Israeli objections, included on its agenda for the first time the “Palestine question” as a separate subject for debate rather than as part of the general question of the Middle East. On November 13 the assembly heard Arafat plead for the Palestinian people’s national rights.
International recognition of the PLO had important repercussions within the Arab camp. At an Arab summit conference held in Rabat, Morocco, on October 26–28, 1974, King Ḥussein accepted a resolution stating that any “liberated” Palestinian territory “should revert to its legitimate Palestinian owners under the leadership of the PLO.” The Rabat decision was denounced by the more radical “rejection front,” composed of the PFLP, the PFLP–GC, the pro-Iraq Arab Liberation Front, and the Front for the Popular Palestinian Struggle, which sought to regain all of Palestine. Although the decision was recognized as enhancing the less extreme position of the PLO elements led by Arafat, the United States continued adamantly to refuse to recognize or deal with the PLO so long as the PLO refused to recognize Israel’s right to exist.
Palestinian guerrilla activity against Israel in 1975 was largely confined to the southern Lebanese border area, where it provoked heavy Israeli attacks from air, land, and sea against Palestinian refugee camps that the Israelis alleged were being used as guerrilla bases. Israeli raids, however, were overshadowed by growing civil strife in Lebanon that developed along Muslim-Christian lines. Civil war between the militias of Lebanon’s sectarian groups erupted in 1975, bringing 15 years of bloodshed, in which more than 100,000 people were killed. The presence of Palestinians was a factor contributing to the civil war, and the war proved disastrous for them.
The PLO initially tried to stay out of the fighting, but by the end of 1975 groups within the overall organization, particularly the “rejection front” groups, were being drawn into an alliance with the Muslim and leftist groups fighting against the Christians. Fighting broke out throughout the country during the first half of January 1976 as Christian forces, foremost the right-wing Maronite Phalange, blockaded the Palestinian refugee camps, and the Palestinian forces and their Lebanese allies responded by attacking Christian villages on the coast. Intense fighting continued, and the PLO, despite all efforts, proved unable to protect the Palestinian population. In August, after a two-month siege, Christian forces killed an estimated 2,000 to 3,000 Palestinians in the Tall al-Zaʿtar camp northeast of Beirut. A peace agreement was negotiated in October 1976. The settlement provided for the creation of a 30,000-member Arab Deterrent Force (ADF), a cease-fire throughout the country, withdrawal of forces to positions held before April 1975, and implementation of a 1969 agreement limiting Palestinian guerrilla operations in Lebanon.
Although the Palestinian guerrillas suffered heavy losses in the Lebanese civil war, they continued to mount attacks against Israel in the late 1970s. Israel again responded with raids into southern Lebanon. In September 1977 Israeli troops crossed into southern Lebanon to support right-wing Christian forces. On March 11, 1978, a Palestinian raid into Israel killed three dozen civilian tourists and wounded some 80 others, and Israel invaded southern Lebanon three days later (Operation Litani). On March 19 the UN Security Council passed resolution 425, calling for Israel to withdraw and establishing the UN Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL). The Israelis withdrew their forces only partially and continued to occupy a strip of Lebanese territory along the southern frontier, in violation of this resolution. They had been only partly successful in their aim of destroying Palestinian guerrillas and their bases south of the Litani River. Several hundred of the Palestinian guerrillas had been killed, but most of them had escaped northward. Estimates of civilian casualties ranged from 1,000 to 2,000.
Under the Likud Party government of the late 1970s and early ’80s, Israel’s settlements in the West Bank grew dramatically, as part of a new Likud policy to maintain strategic dominance in the area. The growth in settlements was accompanied by an increase in Israeli control over the territories, and large parts of those territories were incorporated into Israel’s infrastructure. As this occupation solidified, many local Palestinian leaders turned to building social organizations, labour unions, and religious, educational, and political institutions. The PLO responded by making its presence increasingly felt in the occupied territories, building its own youth groups, providing families with economic assistance, and putting in place a rival political infrastructure that made it possible for PLO-supported candidates to win in the municipal elections of 1976. By the early 1980s the PLO had set up an extensive bureaucratic structure that provided health, housing, educational, legal, media, and labour services for Palestinians both inside and outside the camps. Israeli and Jordanian attempts to encourage alternatives to the PLO failed in the 1980s. Active opposition to Israeli control in the West Bank spread, while frequent demonstrations, strikes, and other incidents occurred, particularly among students.
The late 1970s was a period of more active negotiation on Arab-Israeli disputes. The Arab states supported Palestinian participation in an overall settlement providing for Israeli withdrawal from areas occupied since the 1967 war and establishing a Palestinian state in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. The U.S. position toward the Palestinians showed signs of softening. In March 1977 U.S. President Jimmy Carter spoke of the need for a Palestinian homeland, and he later stated that it was essential for the Palestinians to take part in the peace process. The Israeli cabinet continued to reject the participation of the PLO in the peace process but agreed not to look too closely at the background of Palestinians who might become members of delegations from Arab countries.
In November 1977 the Egyptian president, Anwar Sadat, initiated peace negotiations that led to the agreement known as the Camp David Accords in September 1978 and to the Egyptian-Israeli peace treaty signed on March 26, 1979. Provisions of the accords (named for Camp David, Maryland, U.S., where they were negotiated) included the establishment of a self-governing authority in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip and a transitional period of not more than five years, at the end of which the inhabitants would become autonomous. The Soviet Union during the time of the peace negotiations recognized the PLO as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinians and in 1981 extended formal diplomatic recognition. The nations of western Europe announced their support of PLO participation in peace negotiations in June 1980. The PLO continued to seek diplomatic recognition from the United States, but the Carter administration honored a secret commitment the former U.S. secretary of state Henry Kissinger made to Israel not to deal with the PLO so long as it declined to renounce terrorism and to recognize Israel’s right to exist.
The Likud Party government of Israel viewed the possibility of peace and compromise with suspicion. On June 6, 1982, Israel, claiming that it intended to end attacks on its territory (although a cease-fire had been in effect since July 1981) and aiming to dislodge the PLO and encourage the installation of a Lebanese government friendly to Israel, launched an invasion of Lebanon. PLO and Syrian forces were defeated by Israeli troops, and the remaining PLO forces were contained in west Beirut. After a lengthy siege and bombardment by Israel in July and August 1982, some 11,000 Palestinian fighters were allowed to leave Beirut for various destinations, under international guarantees for their own safety and that of their civilian dependents. Despite these guarantees, however, after Israeli troops had occupied west Beirut, the Phalangists, Israel’s rightist Lebanese allies, were allowed by Israeli forces into the Beirut refugee camps of Sabra and Shatila, where they massacred hundreds (estimates vary between 700 and 3,000) of Palestinian and Lebanese civilians.
Although not all PLO guerrillas were forced to leave Lebanon, the PLO infrastructure in the southern part of the country was destroyed, and Arafat’s departure from Beirut to northern Lebanon marked the effective end of the PLO’s military and political presence in the country. Ultimately, the new government of Lebanon came under the sway of Syria. The dispersal of the PLO from Lebanon significantly weakened the organization’s military strength and political militancy. It was unable to operate freely from any of the nations bordering Israel. Arafat and the other PLO leaders were also threatened by the emergence within Fatah of a faction encouraged by Syria. In December 1983 Arafat was driven out of northern Lebanon by the Syrians and their protégés inside the PLO.
After having established himself near Tunis, Tunisia, Arafat turned once again to diplomatic initiatives. He sought Egyptian and Jordanian support against Syria. He also looked to King Ḥussein as an intermediary for negotiations with the United States and Israel that might lead to a Palestinian ministate on the West Bank within a Jordan-Palestine confederation—an idea that had been favored by the dominant factions in the PLO since the early 1980s. This policy was expressed most concretely in the meeting of the Palestine National Council in Amman in November 1984, the first time it had met there since Jordan had crushed the PLO armed forces in 1970.
Violence escalated from the mid-1980s onward. Rejectionist elements within the PLO renewed their activities, attracting worldwide attention. In October 1985 members of the Palestine Liberation Front, a small faction within the PLO headed by Abū ʿAbbās, hijacked an Italian cruise ship, the Achille Lauro, and murdered one of its passengers. Following an Israeli bombing attack on PLO headquarters near Tunis several days before the hijacking, Arafat moved some departments to Saddam Hussein’s Iraq. Lebanese Shīʿite Muslim groups fought the PLO to stop its reemergence as an armed rival for supremacy in the chaotic situation prevalent in west Beirut and southern Lebanon. West Bank Palestinians demonstrated and engaged in strikes in late 1986.
In Israel several new developments strengthened Palestinian feelings of alienation from the Jewish majority. Jewish ultranationalists increased their demands for more Jewish settlements and the annexation of the West Bank and advocated the forceful removal of the Palestinian Arabs from the occupied territories. The Israeli parliament passed a bill in 1985 banning any political party that endangered state security—i.e., any party that was opposed to Zionism. This reinforced the feeling of most Palestinian citizens of Israel that no legal political party could adequately reflect their national, economic, and political views, although the only party actually banned was the anti-Arab Kach Party. Israelis, especially West Bank settlers, became more antagonistic and militant toward Palestinians as armed attacks against Israel and Israelis living abroad increased in number. Throughout 1986–87, attacks by Palestinians on Israeli settlers and by Israeli settlers on Palestinians mounted. By 1988 more than half of the land in the West Bank and about a third of the land in the Gaza Strip had been transferred to Jewish control, and the Israeli population of the West Bank, mostly concentrated in 15 metropolitan satellites of Tel Aviv–Yafo and Jerusalem, had reached about 100,000.
By the late 1980s a whole generation of Palestinian youth had grown up under Israeli occupation. Nearly three-fourths of Palestinians were younger than 25 years of age. Their political status was uncertain, their civil rights diminished, and their economic status low and dependent on Israel’s economy. Between 100,000 and 120,000 Palestinians crossed daily from the occupied territories into Israel to work. They did not have much faith in Arab governments, nor did they place strong trust in the PLO, which, although still a powerful symbol of Palestinian aspirations, had not succeeded by either diplomatic or military efforts to win Palestinian self-determination. Remittances to family members left behind from those hundreds of thousands who had migrated to Jordan and the Persian Gulf states for work in the 1960s and ’70s were reduced drastically as the economies of many Middle Eastern countries were hit by falling oil prices. Increasingly, Palestinians came to rely on their own efforts.
When the Palestinians saw no improvement in effective support of their aspirations from other countries and no likely favorable change coming from the Israelis, they engaged, throughout 1987, in small-scale demonstrations, riots, and occasional violence directed against Israelis. The Israeli authorities responded with university closings, arrests, and deportations. Large-scale riots and demonstrations broke out in the Gaza Strip in early December and continued for more than five years thereafter. This uprising, which became known as the intifadah (Arabic: “shaking off”), inspired a new era in Palestinian mass mobilization. Masked young demonstrators turned to throwing stones at Israeli troops, and the soldiers responded by shooting and arresting them. Women, and women’s organizations, were prominent. The persistent disturbances, initially spontaneous, before long came under the leadership of the Unified National Command of the Uprising, which had links to the PLO. The PLO soon incorporated the Unified Command, but not before the local leaders had pushed Arafat to abandon formally his commitment to armed struggle and to accept Israel and the notion of a two-state solution to the conflict.
One group, Hamas—an acronym for the Islamic Resistance Movement—challenged the authority of the secular nationalist movement, especially inside Gaza, and sought to take over the leadership of the intifadah. Hamas was an underground offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood, which had built up a network of religious, educational, and charitable institutions in the occupied territories, in addition to establishing an armed wing known as the Sheikh ʿIzz al-Dīn al-Qassām Brigades (named for the nationalist leader killed by the British in 1935). Hamas rejected any accommodation with Israel.
The tactics of the intifadah were highly sophisticated. Union-organized strikes, commercial boycotts and closures, and demonstrations were carried out in one part of the territories, and then, after Israel had reestablished its local power there, they were transferred to a previously quiescent area. Palestinian refugee camps provided major centers for the resistance, but Palestinian Arabs living in more affluent circumstances also participated, and some Palestinian citizens of Israel showed their sympathy with the goals of the uprising. During its first year more than 300 Palestinians were killed, more than 11,500 wounded (nearly two-thirds of whom were under 15 years of age), and many more arrested. Israel closed universities and schools, destroyed houses, and imposed curfews, yet it was unable to quell the uprising. By mid-1990 the International Red Cross estimated that more than 800 Palestinians had been killed by Israeli security forces, more than 200 of whom were under the age of 16. Some 16,000 Palestinians were in prison. By contrast, fewer than 50 Israelis had been killed. Some hundreds of Palestinians in the occupied territories, accused of being collaborators with Israel, were killed by their compatriots. Political paralysis gripped Israel.
Arafat sought to establish himself as the only leader who could unite and speak for the Palestinians, and in mid-1988 he took the diplomatic initiative. At the 19th session of the PNC, held near Algiers on November 12–15, 1988, he succeeded in having the council issue a declaration of independence for a state of Palestine in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Arafat proclaimed the state (without defining its borders) on November 15. Within days more than 25 countries (including the Soviet Union and Egypt but excluding the United States and Israel) had extended recognition to the government-in-exile.
The final weeks of 1988 opened a new chapter in Palestinian-Israeli relations. In December Arafat announced that the PNC recognized Israel as a state in the region and condemned and rejected terrorism in all its forms, including state terrorism, the PLO’s term for Israel’s actions. He addressed a special meeting of the UN General Assembly convened at Geneva and proposed an international peace conference under UN auspices. He publicly accepted UN resolutions 242 and 338, thereby recognizing, at least implicitly, the State of Israel. Despite their ambiguities, UN resolution 242 (1967), which encapsulated the principle of land for peace, and resolution 338 (1973), which called for direct negotiations, were regarded by both parties as the starting points for negotiations. Although Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Shamir stated that he was still not prepared to negotiate with the PLO, the U.S. government announced that it would open dialogue with the PLO.
The approaching end of the Cold War left the Palestinians diplomatically isolated, as did PLO support for Iraqi President Saddam Hussein, who had invaded Kuwait in August 1990 but was defeated by a U.S.-led alliance in the Persian Gulf War (1990–91). Funds from Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the Persian Gulf states dried up. The Palestinian community in Kuwait, which had consisted of about 400,000 people, was reduced to a few thousand. Economic hardship was compounded by the fact that, during the continuing conflict along the Lebanese border and in the occupied territories, Israel imposed severe travel restrictions on Palestinian day laborers. The overall result was loss of jobs, loss of morale, and loss of support for the PLO leadership in Tunis.
However, prospects for a settlement of the outstanding issues between the Palestinians and Israel became significantly altered by several factors: the convening of an international peace conference between Israeli and Arab delegates (including Palestinians from the occupied territories as part of a joint Jordanian-Palestinian delegation) at Madrid in October 1991, sponsored by the United States and the Soviet Union (after December 1991, Russia); the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December; and the replacement, in the Israeli general elections of June 1992, of Shamir and the Likud-bloc government with a Labour Party government that was committed to implementing Palestinian autonomy within a year.
Although progress at the Madrid peace conference was discouraging, secret meetings held in Norway from January 1993 between PLO and Israeli officials produced an understanding known as the Oslo Accords. On this basis, on September 13, 1993, the PLO and Israel signed a historic Declaration of Principles in Washington, D.C. It included mutual recognition and terms whereby governing functions in the West Bank and Gaza would be progressively handed over to a Palestinian council for an interim period of five years, during which time Israel and the Palestinians would negotiate a permanent peace treaty to settle on the final status of the territories.
Despite acts of violence committed by extremist groups on both sides attempting to sabotage the peace process, the Israelis completed their withdrawal from the West Bank town of Jericho and parts of the Gaza Strip in May 1994. On July 1 Arafat entered Gaza in triumph. Four days later he swore in members of the Palestinian Authority (PA) in Jericho, which by the end of the year had assumed control of education and culture, social welfare, health, tourism, and taxation.
Violence and irreconcilable demands by radical elements in the populations of both sides obstructed talks between the PLO and the Israeli government. Nonetheless, on September 28, 1995, Arafat and Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Foreign Minister Shimon Peres signed an agreement in Washington providing for the expansion of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and for elections of a chairman and a legislative council of the PA. The PA would gain control over six large West Bank towns (Janīn, Nāblus, Ṭūlkarm, Qalqīlyah, Ramallah, and Bethlehem) as well as control over most of Hebron. Israel would also gradually redeploy from some 440 villages, which would come under Palestinian rule. Security for those areas would rest with the Palestinian police, although Israeli military forces would be guaranteed freedom of movement throughout the area from which Israel redeployed. Reaffirming the commitment made in the 1993 peace accord, permanent-status negotiations were to be concluded by 1999.
In October 1995, as West Bank villages, towns, and cities were handed over to the PA, right-wing religious and extremist nationalist Israelis stepped up their rhetoric against Rabin and the peace process. On November 4, 1995, Israelis were stunned when Rabin was assassinated by a Jewish extremist. Peres, Rabin’s successor, quickly expressed his determination to continue the planned Israeli deployments.
Elections were held in PA-administered areas in January 1996, in which about three-fourths of Palestinians of the West Bank and Gaza voted. Arafat secured nearly nine-tenths of the vote and assumed the presidency of the PA in February. He also remained chairman of the PLO. Fatah won 55 seats in the 88-seat legislative council. Hamas, however, did not participate in the election and continued its violent opposition to the peace process. The progress toward peace was further cast into doubt when Benjamin Netanyahu, right-wing leader of the Likud Party, was elected prime minister of Israel in May 1996. Netanyahu left office following defeat at the hands of the Labour Party led by Ehud Barak in May 1999. Although Netanyahu reached some accords with the Palestinians, his term in office was marked by increasing mistrust between the two sides.
Subsequent events, however, were a disappointment to all concerned, as a number of negotiating deadlines passed without an agreement. Notable among these was the May 1999 date set as a deadline for a third stage of Israeli military redeployments, an end of the interim period, and a completion of “permanent status” talks on the most contentious issues, such as the status of Jerusalem, the return of refugees, the presence of Israeli settlements in the occupied territories, and the issue of Palestinian sovereignty and statehood.
Also, after a decade of negotiating, eight of those years following the signing of the Declaration of Principles, less than one-fifth of the West Bank (in 15 isolated segments) and about two-thirds of the Gaza Strip had reverted to full Palestinian control. The rest remained under Israeli military occupation (combined with PA civil administration in some areas). The number of Israelis living in West Bank settlements (that now exceeded 150) had grown by some 80,000 in that period, and more Palestinian land had been confiscated in the occupied territories for expanding settlements and for constructing bypass roads reserved solely for use by Israelis. Further, the gross domestic product per capita in Palestinian areas had actually declined in the nine years after the Madrid Peace Conference, Israel restricted the movement of Palestinians (and closed Jerusalem to West Bank and Gaza Strip Palestinians beginning in 1991), and accusations were widespread of corruption within the PA and of human rights abuses by its leaders. All of this made life for most residents of PA-controlled areas worse, in many respects, than it had been before the peace process.
An Israeli-Palestinian summit meeting sponsored by the United States in July 2000 failed to resolve these outstanding issues and led only to an increasingly strained situation. In the aftermath of this summit, a visit to Jerusalem’s Al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (the Temple Mount) in September by Likud leader Ariel Sharon—reviled by Palestinians for his role in the 1982 Sabra and Shatila massacres—was the spark that set off a conflagration. The visit was followed by demonstrations near Al-Aqṣā Mosque the next day, in which Israeli security forces killed and wounded dozens of Palestinian demonstrators. That was the signal for a renewed uprising, which reached a level of violence unseen in the first intifadah, more than 1,000 died in its first 18 months, the overwhelming majority of them Palestinian civilians, and which engulfed the still largely occupied West Bank and Gaza Strip.
Thereafter, suicide bomb attacks by Palestinians in Israeli cities increased. Large numbers of Israelis, most of them civilians, were killed and wounded, and Israeli attacks on PA targets (most located within population centers) raised the already high casualty rate among the Palestinian populace. In the spring of 2002 Israeli troops reoccupied all the towns and cities of the West Bank, reclaiming security control from the PA and tightening restrictions on movement that had earlier been placed on Palestinian residents of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Negotiations reached a complete impasse, and the future of the occupied territories, and of relations between Palestinians and Israelis, became increasingly uncertain. Sharon, blaming Arafat for instigating the attacks against Israel, confined Arafat to his compound in Ramallah from 2001.
In 2003 the PA established the office of prime minister in an effort to circumvent Arafat and restart the peace process with Israel. Arafat installed Mahmoud Abbas, a moderate, in the post. Abbas called for an end to the intifadah, but, feeling that his efforts were thwarted by Arafat, Israel, and the United States, he soon resigned. Following Arafat’s death in 2004, Abbas was elected chairman of the PLO and president of the PA. In 2005 Israel withdrew soldiers and settlers from parts of the West Bank and from all of the Gaza Strip, which then came under Palestinian control. The pullout raised hopes for new peace talks.
In the years that followed, tensions between Hamas and Fatah dominated Palestinian politics. Elections for the Palestinian Legislative Council were held in 2006, and Hamas won a surprise victory over Fatah. Hamas and Fatah eventually formed a coalition government, but violence between their forces escalated in the Gaza Strip. After a week of fighting, Hamas forces defeated Fatah forces and took control of the Gaza Strip, leading Abbas to dismiss the Hamas-led government and declare a state of emergency in June 2007.
The two factions attempted to reconcile a number of times. The first reconciliation agreement was reached in 2011 but failed to bring about much change. A new deal in 2014, in which Hamas agreed to hand over administration of the Gaza Strip to the unity government of the Palestinian Authority Prime Minister Rami Hamdallah, also failed to bring about a significant change. It was not until a 2017 agreement that the PA was able to take control of public institutions in the Gaza Strip, though full control was never achieved and the PA withdrew. In 2019 Hamdallah resigned and the unity government was ended.
Meanwhile, the Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip added a new element of uncertainty to Israeli-Palestinian relations. Israel declared the Gaza Strip under Hamas a hostile entity and imposed a blockade, sealing border crossings and placing heavy restrictions on imports. Hamas rocket attacks on southern Israel became commonplace, as did retaliatory strikes by Israeli forces.
Israel and Hamas agreed in June 2008 to a six-month cease-fire in negotiations brokered by Egypt. When the agreement expired in December, Hamas announced that it did not intend to extend it, and there were accusations of violations by both sides. A major conflict broke out in late December when Israel launched air strikes on Hamas targets in response to increased rocket attacks. A week after commencing the air strikes, Israel mounted a ground offensive into the Gaza Strip. The conflict ended after 22 days, with Israel and Hamas each declaring a unilateral cease-fire. Thirteen Israelis and more than 1,000 Gazans were killed in the fighting.
A round of direct peace talks between Israel and the PA was held in September 2010, but those talks quickly came to a halt over the construction of Israeli settlements in the West Bank. Following the failure of direct talks in 2010, Abbas shifted his efforts toward gaining international recognition for a Palestinian state. In September 2011 he submitted a request to the UN Security Council asking for the admission of an independent Palestinian state to the UN. The action, which was opposed by Israel and the United States, had become necessary, he argued, because the U.S.-mediated peace negotiations had placed too little pressure on Israel to make concessions for peace. The bid for recognition by the Security Council stalled when it became clear that the United States would veto it and that several other members would abstain from voting.
A year after the failure of the Palestinian bid for full membership in the UN, Abbas announced that he would seek the UN General Assembly’s implicit recognition of Palestinian statehood by submitting a draft resolution requesting that the status of the Palestinian mission to the UN (officially called Palestine within the UN) be upgraded from “permanent observer” to “nonmember observer state.” The designation, though falling short of full UN membership, would allow Palestinians to seek membership in international bodies such as the International Criminal Court. The resolution passed on November 29, 2012, with 138 countries in favor, 9 opposed, and 41 abstentions. The resolution also urged Israel and the Palestinians to resume stalled negotiations toward a two-state solution. Israeli officials opposed Abbas’s bid for recognition, saying that such unilateral actions by the Palestinians would hold up negotiations with Israel.
The murders of three teenage yeshiva students in the West Bank in June 2014, for which Netanyahu held Hamas responsible, brought a new escalation of tension. Israeli security forces conducted a massive sweep of the West Bank while exchanging air strikes with rocket fire from militants in the Gaza Strip. On July 8, 2014, Israel launched a large-scale air offensive in the Gaza Strip that targeted militants. After more than a week of bombardment failed to halt rocket fire into Israel, an incursion by Israeli ground troops aimed to destroy underground tunnels and other elements of the militants’ infrastructure. After several weeks of fighting, Israel withdrew its forces from the Gaza Strip, declaring that their mission had been fulfilled.
Some fighting continued until a cease-fire agreement was reached in late August. In exchange for the cessation of rocket fire from the Gaza Strip, Israel agreed to loosen restrictions on goods entering the Gaza Strip, expand the fishing zone off the coast, and reduce the size of the security buffer it enforced in areas adjacent to the Israeli border. Even though more than 2,100 Palestinians died in the 50-day offensive and the Gaza Strip witnessed widespread destruction, leaders of Hamas declared victory for its ability to withstand Israeli attacks and leverage concessions.
In 2017 U.S. Pres. Donald Trump began touting that his administration was devising an “ultimate deal” peace initiative for the Israelis and the Palestinians. The initial optimism with which the Palestinian Authority received Trump and his promised initiative was soon snuffed out by the decision of the United States to move its embassy in Israel to the contested city of Jerusalem in 2018. The United States also began to cut funding to the PA and to aid programs for Palestinians and ordered the closure of the PLO office in Washington, D.C. The peace plan, released in two parts in 2019 and 2020, included predetermined solutions that proposed significant development in the Palestinian territories but favored Israel on the most contentious issues. No negotiations between the Palestinians and the Israelis took place during Trump’s presidency.
Meanwhile, tensions flared along the border of Israel and the Gaza Strip in 2018. A series of protests, in which demonstrators attempted to cross the border into Israel and sent incendiary kites and balloons into Israel, were met with a violent response by Israel. At the peak, on May 14, Israeli soldiers opened fire on protesters attempting to cross the border, killing about 60 people and wounding some 2,700 others. The violence continued to escalate, leading to Israeli air strikes and Hamas rocket fire into Israel.
Both the PA and the Hamas government in the Gaza Strip witnessed unrest in early 2019 as a result of political developments in 2018. In the West Bank the PA attempted to implement a social security program. Because of uncertainties in the PA’s long-term stability and finances, many Palestinians worried that they would pay into the program but never see that money again. The unpopularity of the program led to several protests, culminating in a workers’ strike across the West Bank on January 15, 2019. Meanwhile, attempts at reunifying the administration of the Gaza Strip with the PA fell apart in 2018, leading the PA to cut funding to, and impose sanctions on, the Gaza Strip. Aid from Qatar alleviated some of the financial pressure on Gazans, but the aid was itself offset by new taxes on goods imposed by Hamas. Protests broke out in the Gaza Strip in March 2019 and were met with a brutal response by Hamas.
In late February the PA rejected taxes collected by Israel on its behalf. The rejection was in protest of Israel’s decision to withhold a portion of those funds proportional to the welfare stipend that the PA paid each month to families of Palestinians imprisoned by Israel or killed by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF), a fund which Israel said encouraged violence. After months of severe fiscal strain, the PA began accepting the reduced revenue in late August, but it did not reduce its stipend payments.
Meanwhile, as 2019 progressed, Gazans saw some relief as Israel eased its blockade as it sought to negotiate a long-term understanding with Hamas that would reduce violence. The Egypt-mediated negotiations continued into 2020.
The inauguration of a new U.S. president in 2021 brought hope of a rapprochement between the PA and the United States. Indeed, the United States began restoring aid to the PA and vowed to reopen the PLO office in Washington, D.C. Abbas announced plans to hold parliamentary elections in May and presidential elections in July, which many observers believed were intended to shore up the legitimacy of the Abbas-led government while signaling resolve to renew the peace process. In late April, however, Abbas postponed the elections indefinitely amid concerns that Israel would prevent voting in East Jerusalem—a reason cited for the cancellation of elections in the past.
April also saw renewed tensions in Jerusalem. While Israeli police restricted Palestinians’ access to the Old City for Ramadan tarāwīḥ prayers, both Palestinians and Jews fell victim to street violence. Tensions came to a head in May as the Israeli Supreme Court was set to deliver a ruling on evicting dozens of Palestinian families from their homes in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood. The ruling was delayed amid heightened tensions, but clashes near Al-Aqṣā Mosque led to hundreds of injuries. For the first time since 2014, Hamas launched a barrage of rockets into Jerusalem in response, prompting retaliation from Israeli forces and a conflict that lasted 11 days.
Civil / National Aviation Authority (CAA/NAA)
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film the West Bank, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

