30 Saint Kitts and Nevis

Divided diagonally from the lower hoist side by a broad black band bearing two white, five-pointed stars; the black band is edged in yellow. The upper triangle is green, the lower triangle is red. Green signifies the island’s fertility, red symbolizes the struggles of the people from slavery, yellow denotes year-round sunshine, and black represents the African heritage of the people. The white stars stand for the islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, but can also express hope and liberty, or independence and optimism.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of CIA World Factbook
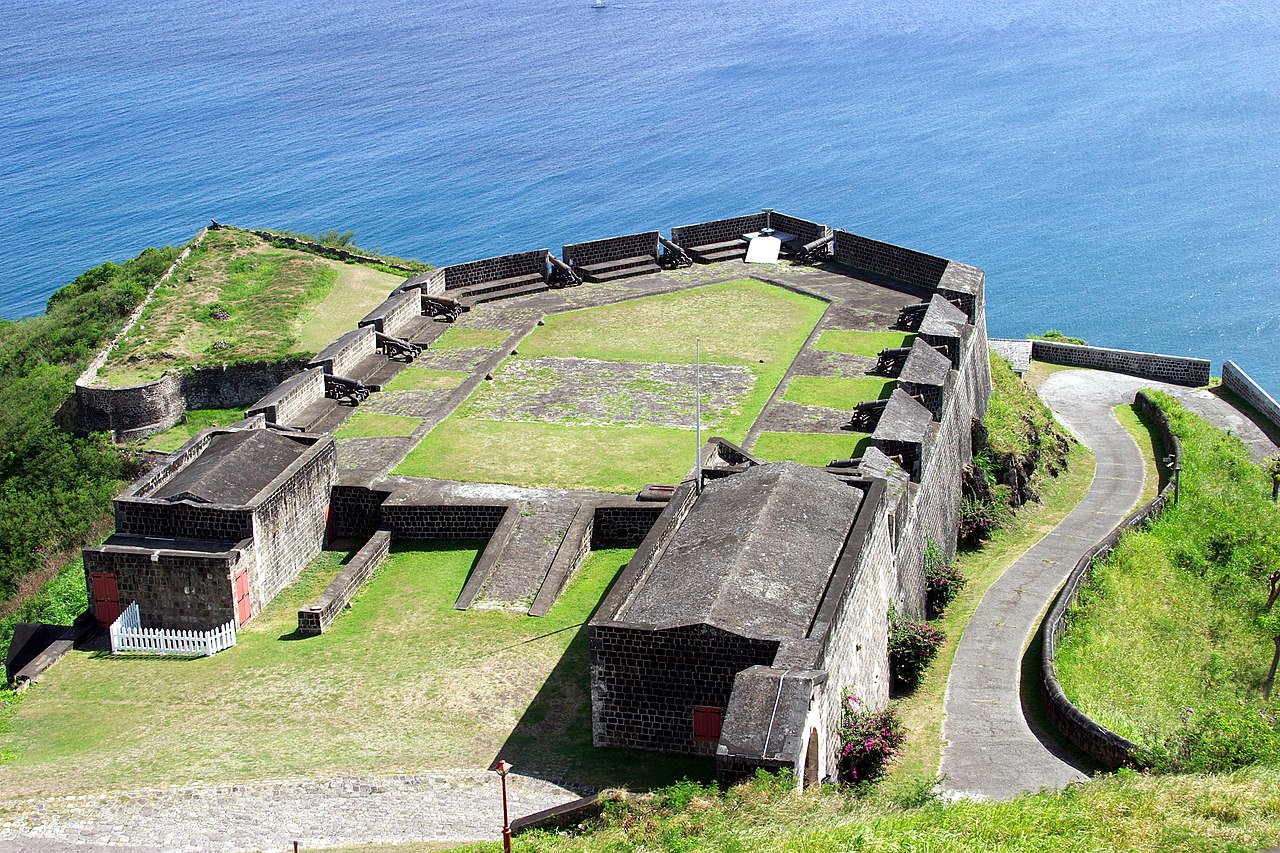

The fortress on Brimstone Hill, focus of the successful French invasion of 1782
Government
According to Britannica, since independence in 1983, the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis has been an independent member of the Commonwealth, with the British monarch as its head of state. An appointed governor-general represents the crown. The prime minister, who together with other ministers is a member of the cabinet, is the head of government. The monarch and the National Assembly constitute the parliament, some of whose members are appointed. The island of Nevis enjoys a certain amount of autonomy within the federal structure; it has its own premier and legislature, and the constitution provides for it to secede from the federation if certain procedures are followed. There is universal adult suffrage.
Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
The Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) is an eleven-member grouping of islands spread across the Eastern Caribbean. Together, they form a near-continuous archipelago across the eastern reaches of the Caribbean Sea. They comprise the Leeward Islands: Antigua and Barbuda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Montserrat, Anguilla and the British Virgin Islands; and the Windward Islands: Dominica, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Grenada, Martinique and Guadeloupe.
Eastern Caribbean Civil Aviation Authority (ECCAA)
The Eastern Caribbean Civil Aviation Authority (ECCAA) evolved from the Directorate of Civil Aviation – Eastern Caribbean States, which may be considered as one of the oldest, if not the oldest institutions in the Eastern Caribbean region. From inception, the Directorate was seen as a vehicle for facilitating a collective and uniform approach to Civil Aviation matters affecting the then Windward and Leeward Islands, which now comprise the OECS Group.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Eastern Caribbean eAIP (requires user name and password)
Drone Regulations
Regulations – defines unmanned aircraft
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone at Brimstone Hill, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

