220 Sierra Leone

Three equal horizontal bands of light green (top), white, and light blue. Green symbolizes agriculture, mountains, and natural resources, white represents unity and justice, and blue the sea and the natural harbor in Freetown.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
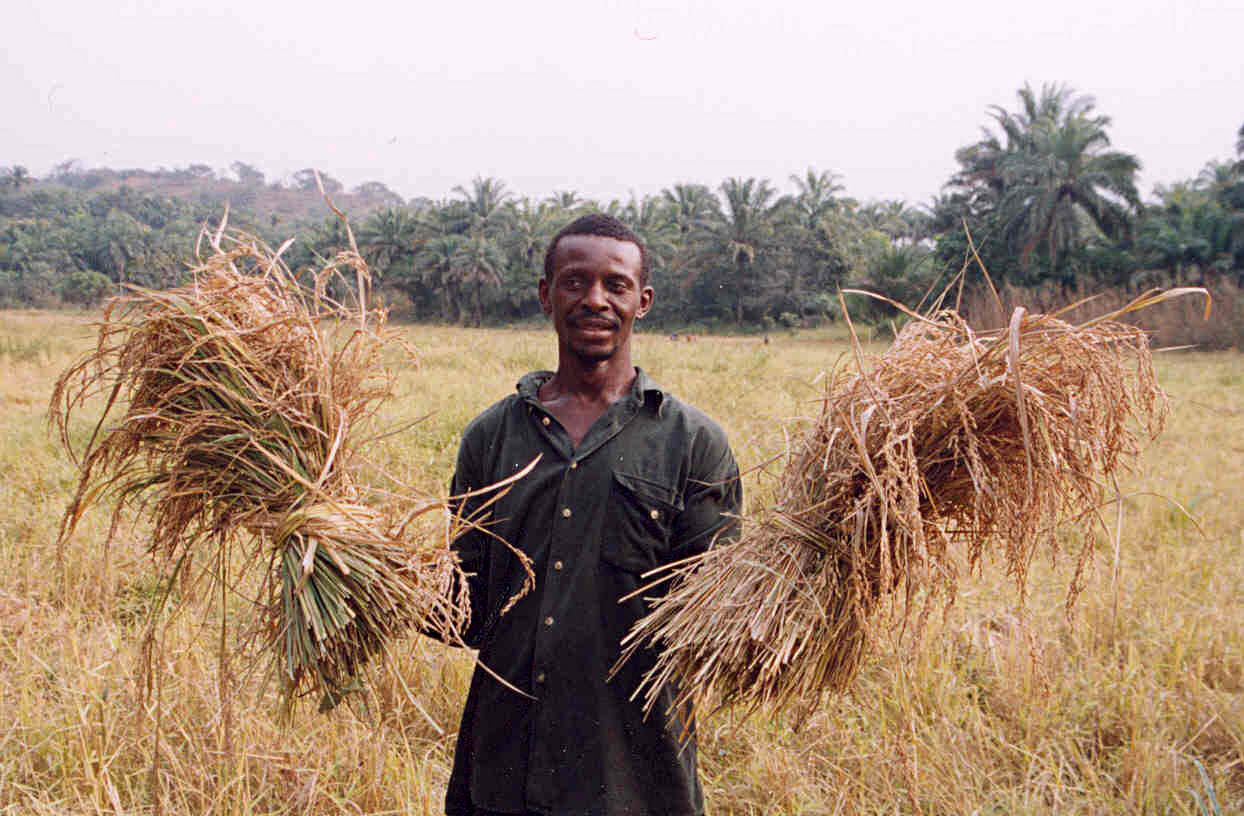

A farmer with his rice harvest in Sierra Leone. Two-thirds of Sierra Leone’s population are directly involved in subsistence agriculture.
Photo courtesy of the Wikipedia
Government
According to Britannica, the constitution of 1971 made Sierra Leone a republic within the Commonwealth. Adoption of the constitution of 1978 created a one-party republic based on the All People’s Congress; the head of state, or executive president, was elected by delegates of the All People’s Congress, and there was a parliament. Mounting political pressures and violence resulted in the adoption of a new constitution in 1991 that established a multiparty system. However, a violent military coup d’état in April 1992 installed a National Provisional Ruling Council (NPRC) and a new head of state. The NPRC subsequently named a cabinet and ordered the dissolution of the House of Representatives and the suspension of the new constitution and all political activity. The NPRC was reconstituted as the Supreme Council of State, and the cabinet was replaced by a council of secretaries in July, establishing stringent military rule. After democratic elections were held in 1996, the 1991 constitution was amended and restored, and the country returned to a multiparty system with an executive presidency and a parliament. The constitution was suspended again after a coup in 1997 but was reinstated the following year.
The country is divided into four administrative units, the Western Area, which was the former crown colony of Sierra Leone, and three provinces (Northern, Eastern, and Southern provinces), which were the former protectorate. The Western Area includes the capital, Freetown. Northern Province is divided into five districts, Southern Province into four, and Eastern Province into three.
The districts are subdivided into chiefdoms, which are controlled by paramount chiefs and chiefdom councillors. The chiefdoms are further divided into sections and villages. The chiefs are hereditary rulers whose local powers have been largely superseded by those of officials of the central and local government. Their influence remains important, however, particularly in matters of traditional culture and justice.
In addition, there are district councils, which in some cases override the chiefdom administrations. The councils deal largely with local matters and are under the indirect control of the central government. Town councils, headed by a mayor, also have been established in the larger provincial towns of Bo, Kenema, Makeni, and Bonthe.
The laws of Sierra Leone follow the pattern of British law. Until 1971 the framework of the courts was equally similar, and the final court of appeal was the Privy Council in London. Since the adoption of a republican constitution, however, the highest court is the Supreme Court, headed by a chief justice.
There are local courts that take account of indigenous laws and customs, magistrates’ courts that administer English-based code, a High Court of Justice, and a Court of Appeal. There are presiding officers in the local, magistrates’, and juvenile courts. The attorney general is also the minister of justice.
Sierra Leone Civil Aviation Authority (SLCAA)
The Sierra Leone Civil Aviation Authority (SLCAA) was established by an Act of Parliament (the Civil Aviation Act, 2008) in April 2008 to provide for an independent professional oversight of international and domestic air transport and cargo services in compliance with international agreements and obligations relating to civil aviation. The establishment of the SLCAA came about after the mandatory Universal Safety Oversight Audit Program (USOAP) conducted by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in May 8 – 12, 2006 and discovered that Sierra Leone was completely deficient in all eight critical elements that were audited.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
Nov 11, 2024 – SLCAA Sets New Rules for Drone Operations in Sierra Leone to Boost Public Safety
2022 – Part 6B – UAS Regulations
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to survey agriculture in Sierra Leone.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

