158 Oman
Three horizontal bands of white (top), red, and green of equal width with a broad, vertical, red band on the hoist side. The national emblem (a khanjar dagger in its sheath superimposed on two crossed swords in scabbards) in white is centered near the top of the vertical band. White represents peace and prosperity, red recalls battles against foreign invaders, and green symbolizes the Jebel al Akhdar (Green Mountains) and fertility.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
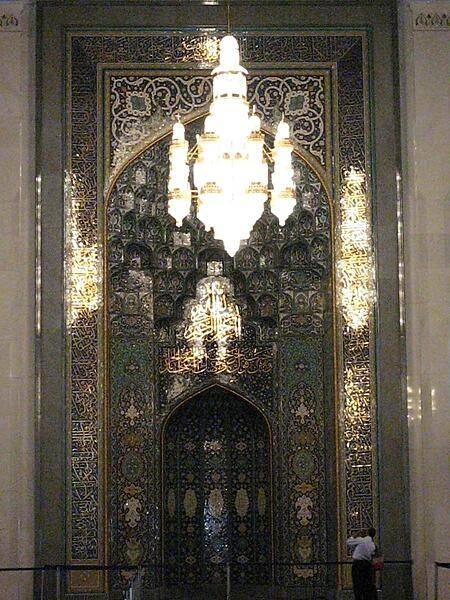
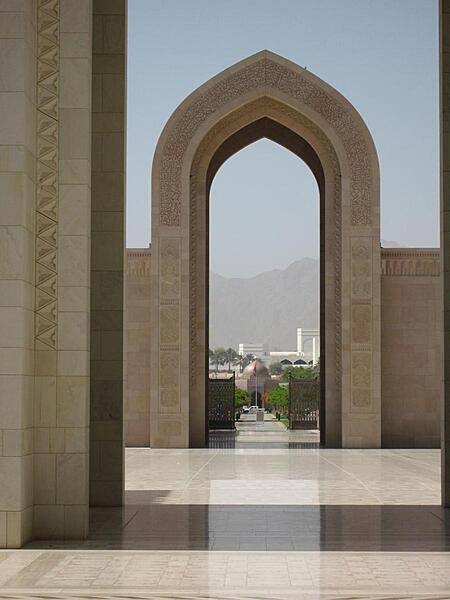


The Grand Mosque in Muscat was commissioned by Sultan Qaboos in 1992. It was inaugurated in 2001 and can accommodate up to 20,000 worshipers. The 70 x 60 m (230 x 197 ft) prayer carpet in the main prayer hall of the Grand Mosque in Muscat is the second largest hand-woven, single-piece carpet in the world and took four years to complete. The primary chandelier, a smaller version of which is shown in this photo, is 14 m (46 ft) tall.
Photos courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Oman is governed by a monarchy (sultanate) with two advisory bodies. The sultan is the head of state, and, although he also acts as the prime minister, he may appoint one if he chooses. The sultan is assisted by a Council of Ministers (Majlis al-Wuzarāʾ), the members of which he typically appoints from among Muscat merchants, informal representatives of interior tribes, and Dhofaris.
The Consultative Assembly, formed by the sultan in 1981, was replaced in 1991 by a Consultative Council (Majlis al-Shūrā), members of which were at first appointed and later elected from several dozen districts (wilāyāt); women from a few constituencies were given the right to serve on the council. In 1996 the sultan announced the establishment of the Basic Law of the State, the country’s first written constitution, which outlined a new system of government that included a bicameral legislature, the Council of Oman. In addition, it clarified the succession process and extended the right to serve to all Omani women. The Council of Oman consists of the Consultative Council as its lower chamber and, as the upper chamber, a new Council of State (Majlis al-Dawlah).
The country is divided administratively into regions (minṭaqāt) and governorates (muḥāfaẓat), each of which contains a number of districts (wilāyāt). Local governance is carried out by a combination of traditional wālīs (representatives of the sultan) and by more recently established municipal councils.
Oman has Islamic courts, based on the Ibāḍī interpretation of the Sharīʿah (Islamic law), which handle personal status cases. There are also civil, criminal, and commercial courts that are organized into courts of first instance, appeals courts, and a Supreme Court, which is chaired by the sultan. In addition, there are some specialized courts.
Civil Aviation Authority (CAA)
Royal Decree No. (33/2012) dated May 26, 2012, established the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) with legal personality and financial and administrative independence so as to be the authority responsible for various regulatory and legislative aspects of the Civil Aviation Affairs in the Sultanate of Oman. And work on the provision of air navigation services and the National Service of Meteorology. The decree was catalytic and supportive to achieving the goals and vision of CAA and achieve the highest levels of safety on air and land. The work of the Commission in the regulatory and service aspects in terms of enacting and implementing regulations and regulations governing civil aviation in the Sultanate of Oman, and the issuance of licenses necessary for crews and stations maintenance, held bilateral air agreements between the Sultanate and other countries, and the development of policies and controls to ensure the security of airports and air transport safety. It set the foundations for the development of revenues of the Sultanate airports and their facilities and maintain those investments and encourage investment opportunities. As for the functions of the service, the body creates and manages the operation and maintenance of air navigation systems development and organization of air traffic and the granting of transit and landing permits, monitoring, inspections and investigations in the field of competence on the institutions and airlines operating in the Sultanate operations.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
CAR 102 – Remote Piloted Aircraft (Drones)
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2025 – Oman: Bids invited to develop national AAM master plan
2025 – Oman prepares for AAM evaluation program
2025 – Oman Will Assess Use Cases For Odys’ Laila Hybrid-Electric VTOL
2025 – Odys Aviation to conduct AAM ecosystem demo in Oman
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the July 2025 Global AAM Forum.
2025 – LYNEports, AeroVecto partner on eVTOL shuttle in Oman
2025 – Lyte, Bluenest, LynePorts to develop vertiports in the Middle East
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the January 2025 Global AAM Forum. Complete session for Day 2 of this Forum is available on the Advanced Air Mobility Institute YouTube Channel
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film the Grand Mosque in Muscat, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

