93 Monaco

Two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white. The colors are those of the ruling House of Grimaldi and have been in use since 1339, making the flag one of the world’s oldest national banners.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
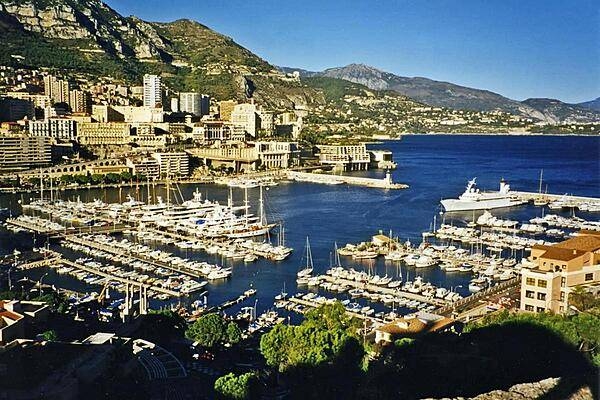

A view of Monte Carlo with the Port of Monaco in the foreground. The ship on the right is that of the prince of Monaco.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, with the fall of Napoleon I, however, the Grimaldis returned; the Congress of Vienna (1815) put Monaco under the protection of Sardinia. The principality lost the neighboring towns of Menton and Roquebrune in 1848 and finally ceded them to France under the terms of the Franco-Monegasque treaty of 1861. The treaty did restore Monaco’s independence, however, and in 1865 a customs union was established between the two countries. Another treaty that was made with France, in 1918, contained a clause providing that, in the event that the Grimaldi dynasty should become extinct, Monaco would become an autonomous state under French protection. A revision to the constitution in 2002 added females and their legitimate children to the line of succession. In 1997 the Grimaldi family commemorated 700 years of rule, and in 1999 Prince Rainier III marked 50 years on the throne. Upon his death in April 2005, he was succeeded by his son, Albert; Albert formally assumed the throne on July 12, 2005. The principality joined the United Nations in 1993. Though not a member of the European Union (EU), Monaco phased out the French franc for the single European currency of the euro by 2002.
Monaco’s refusal to impose income taxes on its residents and on international businesses that have established headquarters in the principality led to a severe crisis with France in 1962. A compromise was reached by which French citizens with less than five years residence in Monaco were taxed at French rates and taxes were imposed on Monegasque companies doing more than 25 percent of their business outside the principality. In the early 21st century, some European nations criticized Monaco’s loose banking regulations, claiming that the principality sheltered tax evaders and money launderers. In 2002 the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) added Monaco to its “blacklist” of uncooperative tax havens. The principality was removed from the blacklist in 2009 after committing to OECD transparency standards.
Monaco’s constitution of 1911 provided for an elected National Council, but in 1959 Prince Rainier III suspended part of the constitution and dissolved the National Council because of a disagreement over the budget. In 1961 he appointed instead a national assembly. The aforementioned crisis of 1962 with France led him to restore the National Council and to grant a new, liberal constitution. The council comprises 18 members, elected by universal suffrage for a term of five years. Government is carried on by a minister of state (who must be a French citizen) and three state councillors acting under the authority of the prince, who is the official chief of state. Legislative power is shared by the prince and the National Council. Since 1819 the judicial system has been based on that of France; since 1962 the highest judicial authority has been the Supreme Tribunal.
Monaco Civil Aviation Authority
The Monaco Civil Aviation Authority, in liaison with the Department of the Environment, is responsible for implementing the process of obtaining Airport Council International Europe carbon accreditation for Monaco International Heliport. The aim of this three-level process is to achieve carbon neutrality. The office deals with:
- The drafting, implementation and monitoring of legislation and regulations on civil aviation
- Managing the air space and the heliport, and supervision of helipads
- Keeping the civil aviation register, monitoring the airworthiness of aircraft, and authorization of air crew licenses
- Supervising aircraft operators and private aircraft
- Monitoring the implementation of bilateral and international agreements on air transport, participating in the work of international organizations in this field to which the Principality belongs
- Monitoring air security and participation in air safety inspections
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
New regulations on use of drones
Ministerial Order No. 2021-532 of August 2, 2021 relating to the conditions of use of unmanned and remotely piloted aircraft, light free balloons, ultra-light gliders and towed aircraft.
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2024 – Blade expands Monaco service with Qatar Airways partnership
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film in Monte Carlo, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

