136 Macau (China)

Green with a lotus flower above a stylized bridge and water in white, beneath an arc of five gold, five-pointed stars: one large in the center of the arc and two smaller on either side. The lotus is the floral emblem of Macau, the three petals represent the peninsula and two islands that make up Macau. The five stars echo those on the flag of China.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
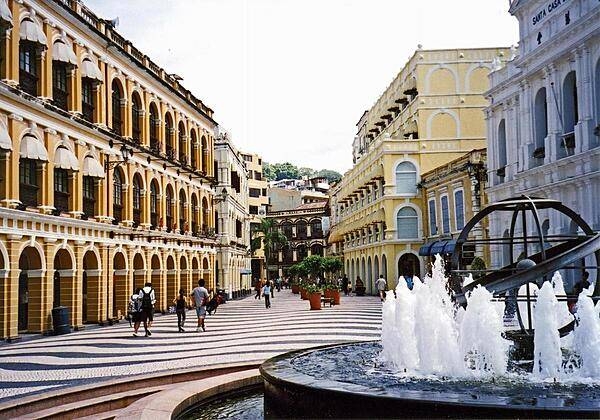

Senate Square with the Leal Senado (Loyal Senate) building on the right.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Last updated on November 5, 2025
Government
According to Britannica, before it became a special administrative region of China in 1999, Macau followed the colonial constitution promulgated in 1976; it was administered by a governor, who in agreement with the Legislative Assembly was appointed by the Portuguese president. With the transfer of sovereignty over the territory to China, the Basic Law of the Macau Special Administrative Region, which outlined a policy of “one country, two systems,” went into effect. For a period of 50 years, Macau will thus retain its capitalist economy and some political autonomy, but foreign policy and defense matters will remain under Chinese administration.
According to the Basic Law, the chief executive, who serves a five-year term, holds executive authority but is under the jurisdiction of the central government in Beijing. An election committee of 300 members, who serve five-year terms, selects the chief executive, who can serve up to two consecutive five-year terms. The chief executive appoints an executive council, which consists of 7 to 11 members, to assist in policy making. The legislature is a single-chamber Legislative Assembly, headed by an elected president and vice president; the assembly has 33 members, who serve four-year terms and are selected by a combination of direct popular election (14), indirect election by a committee of special-interest groups (12), and appointment by the chief executive (7).
Law is based on the Portuguese system. The judicial system was completely administered from Portugal until 1993, when a high court of justice was established in Macau. A new penal code was authorized in 1996 in response to a rise in crime. The Basic Law states that the judicial system remains intact with the transfer of sovereignty and that all judges are appointed by the chief executive. The highest court is the Court of Final Appeal, headed by a chief justice. There are also lower primary courts, intermediate courts, and administrative courts. Macau has a small security force, but defense is the responsibility of the central government in Beijing.
Primary and secondary education in Macau is overwhelmingly at private schools, although the great majority of these schools receive government subsidies. Five years of primary education are officially compulsory, and education is free for children from age 6 to 15. Most receive instruction in Chinese (Cantonese), while the remainder are taught in either English or Portuguese. The University of Macau, formerly the University of East Asia, opened in the early 1990s. In the early 2000s plans were made to move the university from its location on Taipa Island to a parcel of land on China’s Hengqin Island. An agreement for jurisdiction of the land to be transferred to Macau was reached in 2009 as part of a 40-year lease from China. The new campus was inaugurated in 2013, and relocation was completed in 2014. Literacy is now nearly universal in Macau; a slightly larger proportion of males than females is literate.
Civil Aviation Authority (CAA)
The Civil Aviation Authority was established on February 4, 1991 (Decree No. 10/91/M of February 4). It is a public institution with administrative, financial and property autonomy and is subordinate to the Department of Transport and Public Works of the Macau Special Administrative Region. The Civil Aviation Authority is responsible for directing, controlling and supervising civil aviation activities in Macao and the international airspace under the jurisdiction of Macao.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
Drone and Other Flying Activities
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film Senate Square, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

