88 Liechtenstein

Two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red with a gold crown on the hoist side of the blue band. The colors may derive from the blue and red livery design used in the principality’s household in the 18th century. The prince’s crown was introduced in 1937 to distinguish the flag from that of Haiti.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
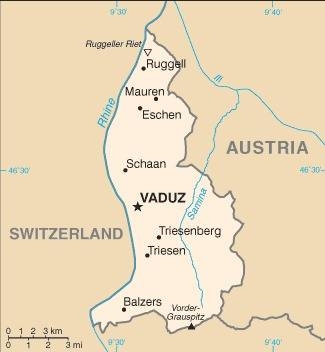
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
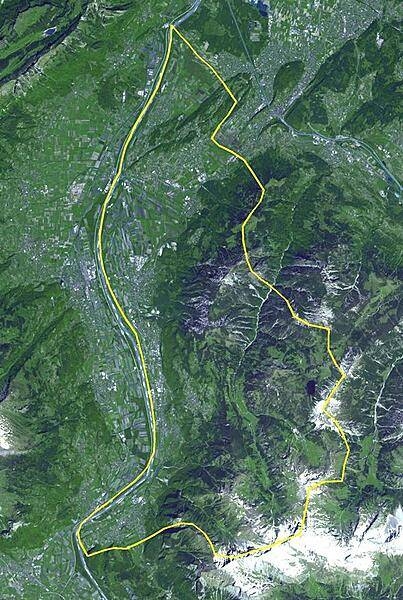
The Principality of Liechtenstein is a landlocked alpine country between Austria and Switzerland; it has an area of 160 sq km (61 sq mi). Despite its limited natural resources, Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens. The image was acquired 21 May 2007 and covers an area of about 19 x 28 km.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Liechtenstein is a constitutional monarchy. Its head of state is the prince, who succeeds to the throne by heredity through the male line as determined by the regulations of the princely house. The constitution of 1921 provides for a unicameral Landtag (Diet), which consists of 25 members elected to four-year terms. The traditional regions of Vaduz and Schellenberg are still recognized as unique regions, the Upper Country (Oberland) and the Lower Country (Unterland), respectively, and they form separate electoral districts. All citizens age 18 or older who live in the principality are eligible to vote in national elections.
The government consists of a prime minister and four other cabinet officials (with at least two officials from each of the two electoral districts), who are appointed by the prince on the recommendation of the Landtag. The 11 Gemeinden (communes) are governed autonomously, but under government supervision, by mayors and city councils, elected every three years. To the south, the more industrial Upper Country contains the communes of Vaduz, Balzers, Triesen, Triesenberg, Schaan, and Planken. The Lower Country, to the north, is divided into the communes of Eschen, Mauren, Gamprin, Ruggell, and Schellenberg. The government maintains a nominal police force, but the standing army was abolished and neutrality proclaimed in 1868 (defense of the principality is the responsibility of Switzerland).
Civil Aviation Office
Civil Aviation Office – The competent aviation authority for Liechtenstein is based on the exchange of notes, the Federal Office of Civil Aviation (FOCA). As a rule, the FOCA deals directly with the applicants or parties to the proceedings. Specific applications or questions concerning ongoing procedures should be addressed directly to the FOCA. The AHR is available for general questions concerning civil aviation issues and acts as a coordination point.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
Drone Laws – follow Swiss Laws
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
Electric aircraft – recall the country follows Switzerland FOCA rules
ICAO State Action Plan on CO2 emission reduction of Switzerland June 2025 – UAM is mentioned in this document
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the January 2025 Global AAM Forum. Complete session for Day 2 of this Forum is available on the Advanced Air Mobility Institute YouTube Channel
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film in Liechtenstein, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

