148 Kuwait

Three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and red with a black trapezoid based on the hoist side. Colors and design are based on the Arab Revolt flag of World War I. Green represents fertile fields, white stands for purity, red denotes blood on Kuwaiti swords, black signifies the defeat of the enemy.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
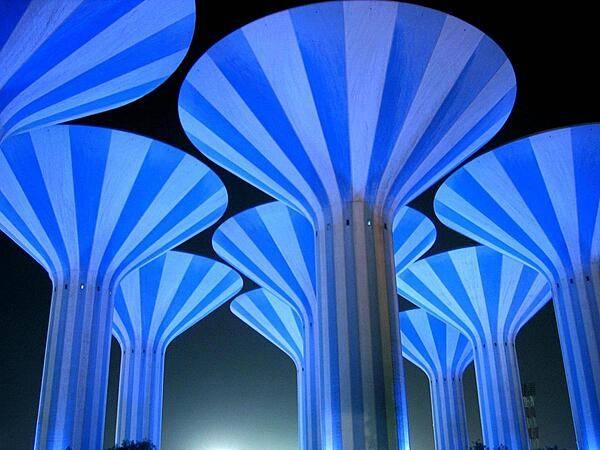

The Kuwait Water Towers: “Mushrooms in the Desert.” There are actually 31 of these aesthetically pleasing water towers in Kuwait City; they were completed in 1976.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Kuwait is a constitutional monarchy with one legislative body. Since gaining independence from Britain in 1961, Kuwait has been governed by an emir from the Ṣabāḥ family. The emir rules through a Council of Ministers, consisting largely of members of his own family, that he himself appoints. Legislative power rests in the National Assembly (Majlis al-Ummah), whose 50 members are elected to four-year terms. This parliament, however, also includes appointed cabinet ministers and has been dissolved several times, including in 1976, 1985, 1999, 2006, and 2009.
Kuwait’s legal system has several sources. Personal and civil law (roughly, family law and probate law) are based largely on Sharīʿah (Islamic law). Commercial and criminal law, while also influenced by Sharīʿah, borrows heavily from both European civil and common law as well as from the legal codes of the Ottoman Empire and from those of other Arab states, which are themselves heavily influenced by European law. There are several lower courts and a system of appeals courts. The emir sometimes acts as the final court of appeal.
Kuwait Civil Aviation Department
In 1956, Kuwait Civil Aviation Department is established as a section of the Directorate of Public Security (later renamed the Ministry of Interior). Two years later Kuwait Airport reports directly to the Civil Aviation Department. Civil Aviation Department decrees Objectives and Aviation Affairs Policy. In 1960, the State of Kuwait becomes a signatory to the International Civil Aviation Chicago Agreement. Kuwaiti business magnates establish private airline Trans Arabia Airways. Announcement of Law No. 30 for organizing Civil Air Navigation, and Law No. 37 for Organizing Aircraft Accidents Investigation. Issue of Amiri Decree inaugurating the Supreme Council of Civil Aviation to handle policy matters relating to the Civil Aviation sector takes place in 1963. Kuwait becomes a full member of both ICAO and World Meteorology Organization (WMO).
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Kuwait AIP – password required
Drone Regulations
Unmanned Aircraft Systems (Drones)
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film at night the Kuwait Water Towers, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

