21 Guyana

Green with a red isosceles triangle (based on the hoist side) superimposed on a long, yellow arrowhead; there is a narrow, black border between the red and yellow, and a narrow, white border between the yellow and the green. Green represents forest and foliage. Yellow stands for mineral resources and a bright future. White symbolizes Guyana’s rivers. Red signifies zeal and the sacrifice of the people. Black indicates perseverance. Also referred to by its nickname The Golden Arrowhead.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of CIA World Factbook
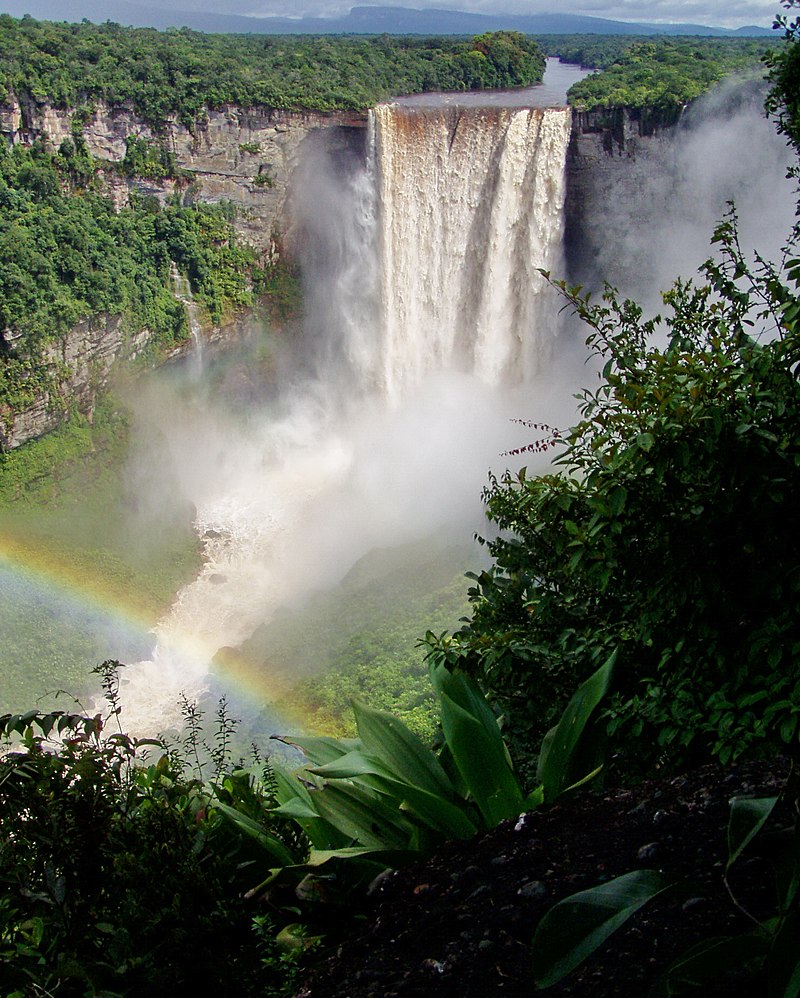

Kaieteur Falls is the world’s largest single-drop waterfall by volume.
Government
According to Britannica, Guyana’s current constitution was promulgated on October 6, 1980. The country’s legislative branch consists of a unicameral National Assembly, with 65 elected members (elected by universal adult suffrage for a term of five years) and three non elected members plus the speaker. Forty members of the Assembly are elected from national party lists under a system of proportional representation; the remaining 25 members are elected by the administrative regions of the country. Executive power is vested in the president, who is the nominee of the party whose slate has received the most votes. The president appoints the cabinet, which is responsible to the National Assembly.
Local government is administered principally through the Regional Democratic Councils, each led by a chairman; they are elected for terms of up to five years and four months in each of the country’s 10 regions. Local communities are administered by village or city councils.
Guyana has two legal traditions, British common law and the Roman-Dutch code, the latter now largely relegated to matters of land tenure. The constitution is the supreme law of the land. The court structure consists of magistrate courts for civil claims of small monetary value and minor offenses; the High Court, with original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters; and the Court of Appeal, with appellate authority in criminal cases. The Court of Appeal and the High Court together constitute the Supreme Court. In 2009 Guyana adopted the Caribbean Court of Justice as its final court of appeal, replacing the Privy Council.
Guyana Civil Aviation Authority (GCAA)
In March of 2002, the Government of Guyana established the Guyana Civil Aviation Authority (GCAA). This was made possible with the passage of the Civil Aviation Act (2000) in parliament of the same year. Formerly known as the Civil Aviation Department within the former Ministry of Public Works and Communications, now the Ministry of Works, the GCAA is responsible for managing and regulating the aviation sector in Guyana, ensuring their compliance with international standards.
The Minister of Works is responsible for the development of civil aviation in Guyana and has direct oversight of the GCAA. The Authority regulates and manages the aviation sector in accordance with the Civil Aviation Act (2018), and the Civil Aviation (Air Navigation) Regulations 2001, Air Transport (Licensing of Air Transport Services) Regulations 2001, The Civil Aviation (Security) Regulation 2004 and Civil Aviation (Air Traffic Services and Rules of the Air) Regulations 2006 made under the act.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to locate missing hikers at Kaieteur Falls, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

