63 Denmark
Red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag. The vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side. The banner is referred to as the Dannebrog (Danish flag) and is one of the oldest national flags in the world. Traditions as to the origin of the flag design vary, but the best known is a legend that the banner fell from the sky during an early-13th century battle. Caught up by the Danish king before it ever touched the earth, this heavenly talisman inspired the royal army to victory. In actuality, the flag may derive from a crusade banner or ensign.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
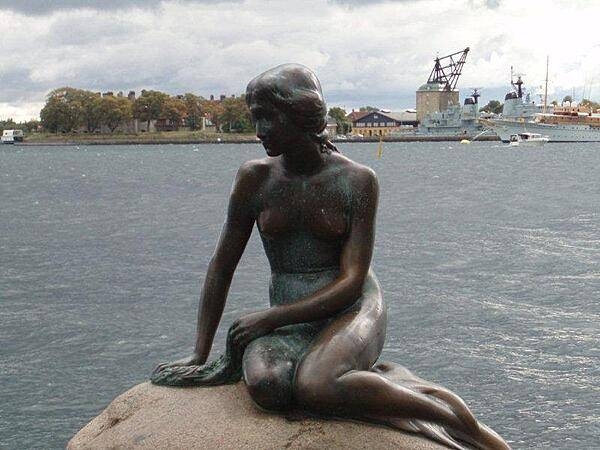

The Little Mermaid statue in Copenhagen Harbor has been a symbol of the city since 1913. Based on the fairy tale of the same name by Danish author Hans Christian Andersen, the small, unimposing, bronze statue has been damaged or defaced many times in the past half century, but has always been restored.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, the constitution of June 5, 1953, provides for a unicameral legislature, the Folketing, with not more than 179 members (including two from the Faroe Islands and two from Greenland). The prime minister heads the government, which is composed additionally of cabinet ministers who run the various departments, such as justice, finance, and agriculture. The ceremonial head of state, the monarch, appoints the prime minister (generally the leader of the largest party or coalition in the Folketing) and the cabinet ministers in consultation with the legislature. The monarch also signs acts passed by the Folketing upon the recommendation of the cabinet sitting as the Council of State. To become law, the acts must be countersigned by at least one cabinet member. Faced with a vote of no confidence, the cabinet must resign.
In addition to establishing unicameralism, the 1953 constitution mandates popular referenda (used, for example, to secure public approval for Danish entry into the EEC, now part of the EU) and postulates the creation of an ombudsman office, the first outside Sweden, its country of origin. The Succession to the Throne Act, which accompanied the 1953 constitution, provides for female succession. This allowed the accession of Queen Margrethe II in 1972.
Before 1970, local government in Denmark was carried out by a system of county council districts, boroughs, and parishes. A reform in that year reduced the number of counties and replaced the boroughs and parishes with a system of municipalities. In 2007 a further reform replaced the counties with a small number of administrative regions, which encompass the various municipalities. Regions and municipalities are governed by elected councils.
Most criminal charges and civil disputes fall within the jurisdiction of district courts. Two High Courts hear appeals from the district courts and serve as courts of original jurisdiction in serious criminal cases, in which 12-person juries are impaneled. In some nonjury criminal cases, lay judges sit alongside professional judges and have an equal vote. The Special Court of Indictment and Revision may reopen a criminal case and order a new trial. In Copenhagen there is a Maritime and Commercial Court, which also uses lay judges. The Supreme Court sits at the apex of the legal system.
Danish Civil Aviation and Railway Authority
Danish Civil Aviation and Railway Authority is organized with an Executive Management Board and two sectoral centers with including offices. And in addition to that, Bornholm Airport, Taxation Secretariat and Mink Secretariat.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Naviair
Naviair has been designated by the Danish Civil Aviation and Railway Authority to provide air navigation services.
They share some material on drones on their website. You should check out this interactive map.
Drone Regulations
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
Bilateral agreements facilitate the reciprocal airworthiness certification of civil aeronautical products imported/exported between two signatory countries. A Bilateral Airworthiness Agreement (BAA) or Bilateral Aviation Safety Agreement (BASA) with Implementation Procedures for Airworthiness (IPA) provides for airworthiness technical cooperation between the FAA and its counterpart civil aviation authorities.
Reciprocal acceptance of aviation safety-related approvals and services with the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and Member States of the European Union are primarily governed by the U.S. – European Union Safety Agreement.
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the July 2025 Global AAM Forum.
2025 – Copenhagen Helicopter and Crisalion Plan Island-hopping eVTOL Flights
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the January 2025 Global AAM Forum. Complete session for Day 1 of this Forum is available on the Advanced Air Mobility Institute YouTube Channel
2023 – HCA Airport and Copenhagen Helicopter partner on vertiport development in Denmark
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film in Copenhagen, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

