60 Bulgaria

Three equal horizontal bands of white (top), green, and red. The pan-Slavic white-blue-red colors were modified by substituting a green band (representing freedom) for the blue.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
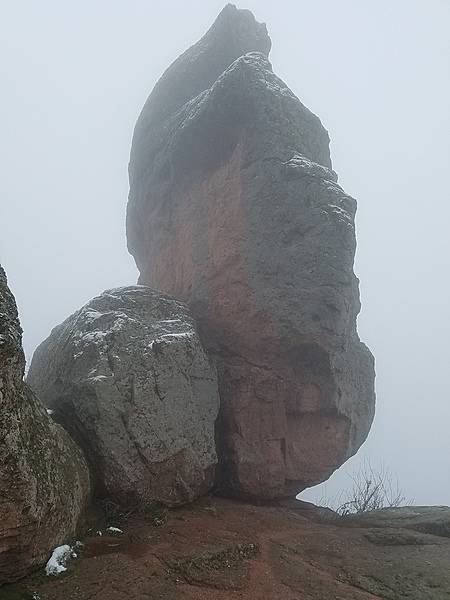

Belogradchik Rocks near Vidin. Each of the limestone rocks has its own name.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, in July 1991 the National Assembly adopted a new constitution establishing a parliamentary government and guaranteeing direct presidential elections, separation of powers, and freedom of speech, press, conscience, and religion. New laws allowed for the return of the properties that had been confiscated by the previous communist governments. Other laws aimed at meeting EU standards were passed, including those regarding competition, foreign investment, intellectual property rights, and a commercial code.
Under the terms of the 1991 constitution, Bulgaria is a parliamentary republic, i.e., the prime minister is elected by the majority party (or coalition of parties) in the National Assembly (parliament). The president, who is elected for a five-year term, is the head of state. The president schedules national referenda and elections for the National Assembly, serves diplomatic and other functions, and promulgates and can veto laws.
According to the constitution, the nation’s governing body, the Council of Ministers, is proposed by the president in consultation with the various groups of the National Assembly and with the majority party’s candidate for prime minister. Comprising the prime minister, deputy prime ministers, and ministers, the Council of Ministers is charged with coordinating and overseeing the implementation of policies on both domestic and foreign issues in accordance with the constitution and laws of Bulgaria.
The National Assembly, a unicameral, representative body composed of 240 members, constitutes the legislative branch of the government. It passes and amends laws, ratifies treaties, levies taxes, and retains the power to pass a motion of no confidence in the Council of Ministers or the prime minister, thereby compelling the resignation of the council. Members of the National Assembly serve four-year terms.
Township councils embody state power at the local government level. The members of the township councils are elected by the inhabitants of the township to four-year terms. Executive power at the level of local government lies with the elected mayor of a township. Between the township and state levels of government is the oblast, or province, government.
The court system consists of the Supreme Court of Cassation, the Supreme Administrative Court, local courts, courts of appeal, and military courts. The constitution provides that specialized courts may also be established. At the head of the prosecutorial structure is the prosecutor general.
The High Judicial Council, consisting of 25 members, appoints judges, prosecutors, and investigators. The members of this council are appointed by the National Assembly and judicial authorities. The Constitutional Court, composed of 12 justices (each of whom serves a nine-year term), is charged with interpreting the constitution and ruling on the legality of measures passed by the National Assembly. The parliament, the president, and the supreme courts each appoint four justices.
Directorate General of Civil Aviation Administration
Member States of the European Union are obliged to establish a National Supervisory Authority (NSA) in order to carry out the tasks assigned to such a body under Single European Sky Legislation. In order to implement the provisions of the regulations for the Single European Sky, the Republic of Bulgaria with amendment of Art. 16c of the Civil Aviation Act, designated the Directorate General of Civil Aviation Administration as the National Supervisory Authority (NSA) with regard to the safe and effective operation of air navigation service providers.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
BULATSA
The Air Traffic Control Department provides aviation users with access to the Aeronautical Information and Publication (AIP) of the Republic of Bulgaria, aeronautical meteorological services, airspace utilization plan and VFR flight planning.
Drone Regulations
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
Bilateral agreements facilitate the reciprocal airworthiness certification of civil aeronautical products imported/exported between two signatory countries. A Bilateral Airworthiness Agreement (BAA) or Bilateral Aviation Safety Agreement (BASA) with Implementation Procedures for Airworthiness (IPA) provides for airworthiness technical cooperation between the FAA and its counterpart civil aviation authorities.
Reciprocal acceptance of aviation safety-related approvals and services with the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and Member States of the European Union are primarily governed by the U.S. – European Union Safety Agreement.
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the July 2025 Global AAM Forum.
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the January 2025 Global AAM Forum. Complete session for Day 1 of this Forum is available on the Advanced Air Mobility Institute YouTube Channel
2023 – Eurocontrol delivers workshop to provide U-space guidance and support in Sofia, Bulgaria
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film the limestone rocks in Vidin, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

