10 Brazil

Green with a large yellow diamond in the center bearing a blue celestial globe with 27 white five-pointed stars. The globe has a white equatorial band with the motto ORDEM E PROGRESSO (Order and Progress). The current flag was inspired by the banner of the former Empire of Brazil (1822-1889). On the imperial flag, the green represented the House of Braganza of Pedro I, the first Emperor of Brazil, while the yellow stood for the Habsburg Family of his wife. On the modern flag the green represents the forests of the country and the yellow rhombus its mineral wealth (the diamond shape roughly mirrors that of the country). The blue circle and stars, which replaced the coat of arms of the original flag, depict the sky over Rio de Janeiro on the morning of 15 November 1889 – the day the Republic of Brazil was declared. The number of stars has changed with the creation of new states and has risen from an original 21 to the current 27 (one for each state and the Federal District).
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
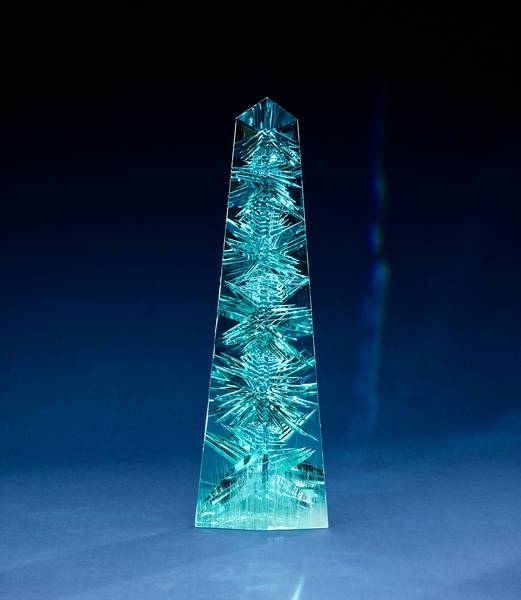

Aquamarine, often called the treasure of mermaids, is mostly found and mined in Brazil, as well as countries that fall along the Mozambique geological belt in Africa. The biggest aquamarine ever found was in Brazil in 1910, it weighed 110 kg ( 243 lb) and was cut into smaller faceted stones for jewelry. The “Dom Pedro,” the largest single piece of cut-gem aquamarine in the world, was found in a Brazilian pegmatite mine in the late 1980s and is named after Brazil’s first two emperors (both named Pedro). The original crystal weighed roughly 45 kg (100 lb), but during excavation it shattered into three pieces. The largest section, approximately 27 kg (60 lb), was sculpted into an obelisk shape. The obelisk, 35.5 cm (14 in) tall, measuring 10 cm (4 in) across the base and weighing 10,363 carats or 2.1 kg (4.6 lbs), is part of the permanent collection of Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, DC.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Brazil is a federal republic divided into 26 states and the Federal District (Distrito Federal), the latter including the capital city, Brasília. Since 1934 the nation has had universal suffrage. In 1988 Brazil promulgated a new constitution—the eighth since the country’s independence in 1822—that abolished many traces of the military regime (1964–85), defined civil rights, and outlined the functions of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. It restricted the president’s power to legislate, proscribed government censorship of the arts, condemned the use of torture, prohibited extradition for political crimes, set the minimum voting age at 16 years, and allowed the federal government to intervene in state and local affairs. The constitution has been amended several times since its promulgation, but some of the changes have been temporary, with specifically designated timespans.
Legislative power is exercised by the bicameral National Congress (Congresso Nacional), comprising the Chamber of Deputies (Câmara dos Deputados) and the Federal Senate (Senado Federal). Congress meets every year in two sessions of four and a half months each. The constitution gives Congress the power to rule in matters involving the federal government, particularly those related to fiscal policies and to the administration of the union. Congress also ratifies international treaties negotiated by the executive, authorizes the president to declare war, and decides whether or not the federal government may intervene in the affairs of the states. If the president vetoes a congressional bill or any of its provisions, Congress has 30 days to overrule the veto by an absolute majority vote.
The Chamber of Deputies consists of representatives of the states elected every four years by direct universal suffrage. The number of deputies is in rough proportion to the population of each state, but no state can be represented in the chamber by more than 70 or by fewer than eight deputies. This system grants a disproportionate share of political power to the states of the Northeast and North and severely underrepresents the heavily populated state of São Paulo.
The 81-seat Federal Senate is composed of three representatives from each state and the Federal District who serve eight-year terms. Senatorial elections are held every four years, alternating between one-third (27) and the remaining two-thirds (54) of the seats. Senators are directly elected by the residents of each state.
Executive power is exercised by the president, who is head of state and government, is directly elected to a four-year term (and is eligible for one reelection), and appoints a cabinet of various ministers of state and several other heads of ministerial-level departments. The executive has wide powers, particularly in economic and foreign policy, finances, and internal security. The president can submit bills to Congress and request legislative approval within 30 days; if Congress does not comply within this period, the bill is considered approved. The president can partly or totally veto any bill submitted by Congress in addition to issuing provisional measures that remain in effect for 30-day periods. The president is also commander in chief of the armed forces; in practice, however, civil-military relations in Brazil have never been taken for granted.
The Brazilian judicial system is divided into two branches: the ordinary branch, made up of state and federal courts, and the special branch, made up of labor, electoral, and military courts.
The Supreme Federal Court (Supremo Tribunal Federal) is Brazil’s highest court. It is composed of 11 members nominated by the president with the approval of the Federal Senate. The court provides final rulings on constitutional issues and hears cases involving the president, the vice president, Congress, the judiciary, the attorney general, government ministers, diplomats, foreign countries, and the political or administrative divisions of the union.
The Higher Court of Justice (Superior Tribunal de Justiça) consists of 33 judges appointed by the president with the approval of the Senate. It is the highest court in the land regarding non constitutional matters and also hears cases involving governors of the states and the Federal District. The ordinary branch also includes federal courts of appeal known as Regional Federal Courts. Each state has state and federal courts that exercise first-instance jurisdiction.
Of the special branch courts, electoral courts are responsible for the registration of political parties and the control of their finances. They also select the date of elections and hear cases involving electoral crimes. Labour courts mediate in conflicts between management and workers, and military courts have jurisdiction in cases involving members of the armed forces.
Although the Brazilian judicial system has long been criticized for inefficiency, incidents of political favoritism, and widespread corruption, efforts have been made to reform it, including, most notably, the adoption in 2004 of Constitutional Amendment 45. That amendment established the principle of stare decisis, under which high courts’ decisions were to be considered binding precedents, with the intention of increasing the efficiency of lower courts. The amendment also created the National Council of Justice, an external institution to oversee compliance with judicial rules and to consider complaints against judges. Within the country’s prisons, harsh and overcrowded conditions have often incited mass escape attempts and riots, during which many prisoners have been killed.
The federal government does not provide for separate regional administrations, although it promotes economic growth in the poorer regions through agencies known as the superintendencies for the development of the Northeast, or SUDENE (founded 1959), and of the Amazon region, SUDAM (1966). SUDENE and SUDAM grant federal funds to development projects and oversee tax incentives that are intended to stimulate local and regional investment; however, the policies of the agencies have varied significantly under different federal administrations, and agency functions frequently overlap, especially at the local level.
The states are semi-autonomous with their own constitutions, justice systems, and directly elected governors and legislative assemblies. The Federal District has been administered by a directly elected governor since the 1990s; previously, the president had appointed a mayor (prefeito) to oversee the district.
Brazil is also subdivided into more than 5,000 municipalities (municípios) that are created by the states according to federal guidelines. The municipalities, which are similar to counties and may cover urban or rural zones, have their own fiscal resources and autonomous governments, including directly elected mayors and municipal councillors. Major cities are generally state capitals, and relations between governors and mayors are often pervaded by bureaucratic rivalries.
National Civil Aviation Agency (ANAC)
ANAC is a regulatory agency which was established to regulate and inspect civil aviation activities as well as aeronautical and airport infrastructure in Brazil. The agency was created in 2005, replacing the Department of Civil Aviation (DAC) as the new National Civil Aviation Authority. The Agency is responsible for the regulation, inspection and certification of aircraft, companies, manufacturers, aircraft maintenance organizations, aerodromes, schools, and civil aviation professionals. The government agency works to ensure civil aviation safety and security and to improve the quality of services, fostering a competitive market. ANAC is linked to the Ministry of Infrastructure, however it is not hierarchically subordinate to the Ministry, and it has administrative independence, financial autonomy, and fixed mandate for its directors.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
DECEA
The Department of Airspace Control (DECEA) is the organization responsible for controlling Brazilian airspace, provider of air navigation services that enable flights and the ordering of air traffic flows in the country.
The mission of the Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) Portal is to gather the legislation and information necessary for pilots and UAS operators to carry out safe operations and in line with the regulatory framework in force, as well as provide the user with a request channel for access to Brazilian airspace.
Drone Regulations
ANAC has established the rules for the operation of civilian unmanned aircraft, also known as drones, in Brazil.
ANAC Brazilian Civil Aviation Special Regulation No. 94 (RBAC-E No. 94) is complementary to the rules established by the Department of Airspace Control (DECEA) and the National Telecommunications Agency (ANATEL).
Register your drone/model aircraft
SARPAS is a system developed by the Department of Airspace Control (DECEA) with the objective of making it possible to request access to Brazilian airspace for the use of Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS), that is, drones, contributing to safe flights. and within the norms.
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
Bilateral agreements facilitate the reciprocal airworthiness certification of civil aeronautical products imported/exported between two signatory countries. A Bilateral Airworthiness Agreement (BAA) or Bilateral Aviation Safety Agreement (BASA) with Implementation Procedures for Airworthiness (IPA) provides for airworthiness technical cooperation between the FAA and its counterpart civil aviation authorities.
Bilateral Aviation Safety Agreement – Executive Agreement
Implementation Procedures for Airworthiness – Signed Original Documents
Implementation Procedures for Airworthiness (Revision 2) (Effective July 31, 2019)
Revision 2 combined with Amendments 1, 2 and 3 to Revision 2:
FAA-ANAC Bilateral Engagement Roadmap (Issue 2)
2016 Notification of Policy Deviation Memorandum for FAA Order 8130.21H
Letter of Intent for Cooperation in Electric Vertical Take-off and Landing (eVTOL) Aircraft
Flight Standards Agreements
Maintenance Agreement Guidance (MAG)
Maintenance Implementation Procedures (MIP)
FAA – ANAC Entry into Force Notification
Obtaining Certification Approval from this Country
2025 – Anac Opens Sectoral Consultation on Safety Objectives for eVTOL Aircraft
2025 – EVE eVTOL airworthiness criteria published
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2025 – Embry‑Riddle, Brazilian Researchers to Tackle Challenge of Keeping Electric Aircraft Cool
2025 – Eve, InvestSP focus on eVTOL regulations, infrastructure in Brazil
2025 – ANAC looks to speed Eve air taxi certification
2025 – Eve Raising $230 Million To Support eVTOL Aircraft Development
2025 – Líder To Represent Beta Technologies in Brazil
2025 – FFG places eVTOL aircraft order with Eve Air Mobility
2025 – Air Taxi Group Revo Kickstarts Paris Show Order Spree
2025 – Revo orders up to 50 eVTOL aircraft from Eve
2025 – Safran to equip Eve eVTOL with distress beacons
2025 – Eve Air Mobility secures Brazilian FINEP grant
2025 – Eve, UI Helicopter to collaborate on AAM in South Korea
2025 – ANAC selects teams to establish vertiport regulations in Brazil
2025 – UrbanV, PAX Aeroportos to establish eVTOL testing area in Brazil
2025 – ANAC approves commercial operations of Sprayhawk UAV in Brazil
2025 – Eve, VertiMob, PRS partner on ANAC consortium
2025
Video courtesy of Advanced Air Mobility Institute from the January 2025 Global AAM Forum. Complete session for Day 1 of this Forum is available on the Advanced Air Mobility Institute YouTube Channel
2024 – Michaelis to build vertiport, evaluate eVTOL aircraft at SBGL in Brazil
2024 – São Paulo Moves Closer to eVTOL Future with Successful Air Traffic Test
2024 – Brazilian city emerges as hub for AAM in South America
2024 – Embraer’s Eve Air Mobility is building full-scale eVTOL Prototypes
2024 – BNDES approves $88M loan for Eve Air Mobility facility in Brazil
2024 – First Flight of EH216-S Pilotless eVTOL in Brazil
2024 – ANAC issues experimental flight certificate for EHang EH216-S
2024 – ANAC proposes rules for VTOL aircraft pilot licensing, rating
2023 – Eve Air Mobility’s eVTOL Airworthiness Criteria Released for Public Consultation
2023 – Helisul Aviation to purchase 50 Moya eVTOL aircraft
2023 – ANAC presents an unprecedented panorama on Advanced Air Mobility and eVTOLs
2022 – Airports In Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador & Uruguay Could Become eVTOL Hubs
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone in Brazil.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in, and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

