204 Liberia
11 equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white. A white five-pointed star appears on a blue square in the upper hoist-side corner. The stripes symbolize the signatories of the Liberian Declaration of Independence. The blue square represents the African mainland, and the star represents the freedom granted to the ex-slaves. According to the constitution, the blue color signifies liberty, justice, and fidelity, the white color purity, cleanliness, and guilelessness, and the red color steadfastness, valor, and fervor.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
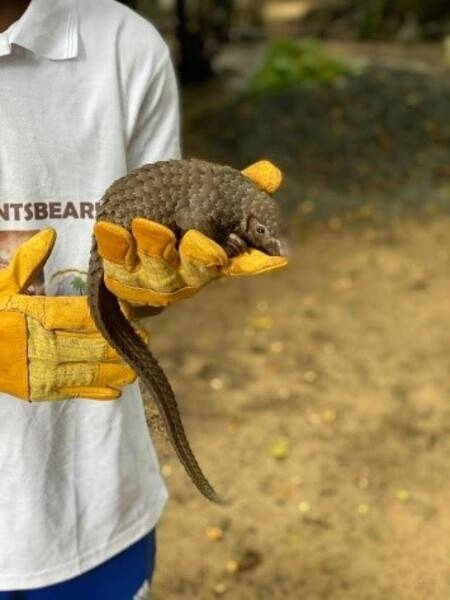

The Liberia Wildlife Sanctuary rescues animals, such as this pangolin, from being poached for bushmeat or sold or kept as pets. The ultimate goal of the Sanctuary is releasing the animals back into the wild or more protected areas.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Liberia’s government was patterned after that of the United States, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches. Political parties were legalized in 1984, and civilian rule was established in 1986. However, considerable political unrest and violence precluded any stable leadership in power from the mid-1990s to the early 2000s. A power-sharing agreement in 2003 largely ended the fighting and created a National Transitional Government (NTG). The NTG, supported by United Nations peacekeeping troops, replaced the government under the 1986 constitution and ruled until a democratically elected administration was installed in 2006.
Liberia is a multiparty republic. Under the 1986 constitution, the head of state and government is the president, who is directly elected for a six-year term. Members of the bicameral National Assembly, who serve six-year terms in the House of Representatives and nine-year terms in the Senate, are also elected directly.
For administrative purposes, Liberia is divided into 15 counties. Each of the counties is headed by a superintendent, who is appointed by the president.
The judicial system comprises the Supreme Court, an appeals court, magistrate courts, and criminal courts. There are also traditional courts in some communities; the ethnic groups are allowed, as far as possible, to govern themselves according to customary law.
Liberia Civil Aviation Authority (LCAA)
The Bureau of Civil Aviation witnessed a departmental shift from the Ministry of Commerce Industry & Transportation and later the decoupled Ministry of Transport until 2005 after the legislative determination, which created the independent Liberia Civil Aviation Authority (LCAA). The mandate of the LCAA is to provide for the regulation and promotion of civil aviation in Liberia, to foster its safe and orderly development, and for other purposes incidental thereof.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Drone Regulations
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone to film the Liberia Wildlife Sanctuary, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

