38 Fiji

Light blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant and the Fijian shield centered on the outer half of the flag. The blue symbolizes the Pacific Ocean and the Union Jack reflects the links with Great Britain. The shield – taken from Fiji’s coat of arms – depicts a yellow lion, holding a coconut pod between its paws, above a white field quartered by the cross of Saint George. The four quarters depict stalks of sugarcane, a palm tree, a banana bunch, and a white dove of peace.
Flag courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Map courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
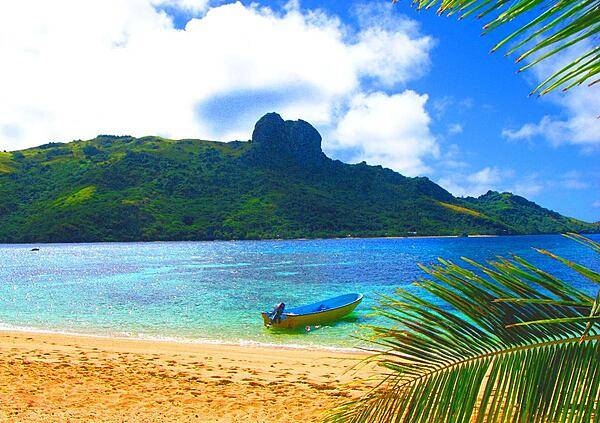

A beach on the island of Kuata, the smallest of the Yasawa Islands Group. Tourism is of growing importance to the island’s economy; its deep lagoon is excellent for swimming and snorkeling.
Photo courtesy of the CIA World Factbook
Government
According to Britannica, Fiji is governed under a constitution adopted in 2013. The country’s first constitution was promulgated in 1966, four years before Fiji achieved independence from Great Britain. Until 1987, Fiji was a dominion, a member of the Commonwealth, and a parliamentary democracy with a government led by an elected president. The government was overthrown twice in 1987 in military-led coups, and in October that year Fiji was expelled from the Commonwealth (though it was readmitted in 1997) and became a republic.
A new constitution took effect in 1990 and was revised in 1997. It provided that the prime minister, the head of government, be appointed by the president, who in turn was appointed by the Bose Levu Vakaturaga (Great Council of Chiefs), a body composed of the hereditary leaders of the 70 major Fijian clans. It also called for a House of Representatives and a Senate. After yet another military coup in 2006, the 1997 constitution was declared to be still in effect, but in practice the government consisted of a non elected interim government, led by a prime minister who was also the commander of the military. The president was the head of state and was advised by an interim cabinet. In 2009, after a Fijian high court ruled that this governmental regime was illegal, the president assumed all power and abrogated the 1997 constitution. In March 2012 the president abolished the Bose Levu Vakaturaga.
The current constitution was promulgated in September 2013. As with previous constitutions, the head of government is the prime minister, who is the leader of the majority party in the national legislature. The head of state is again the president, who serves a maximum of two terms of three years each. The president is appointed by Parliament, which chooses between a candidate nominated by the prime minister and one nominated by the leader of the opposition. The constitution calls for a unicameral 50-member Parliament whose members are elected by proportional representation. The number of seats may increase or decrease in proportion to the size of the country’s population. Members are elected to four-year terms by universal adult (18 years and older) suffrage. Among the country’s registered political parties are FijiFirst, the Fiji Labour Party, the National Federation Party, the People’s Democratic Party, and the Social Democratic Liberal Party (Sodelpa).
Local government reflects the pluralism of Fiji’s social structure. There are elected multiethnic councils in the larger towns, a separate Fijian administration incorporating a hierarchy of chiefs and councils for the control of rural Fijians, and direct administration elsewhere.
Civil Aviation Authority of Fiji (CAAF)
The Civil Aviation Authority of Fiji (CAAF) is the national aviation authority in the Republic of Fiji and is responsible for discharging functions on behalf of the Government of Fiji under the States responsibility to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, also known as the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). CAAF regulates, certifies and licenses airline operators, airport operators, air traffic and air navigation service providers, aviation security service providers, pilots, aircraft engineers, air traffic controllers, technicians, airline contracting organizations, and international air cargo operators in Fiji and abroad and conducts surveillance of these entities.
Pacific Aviation Safety Office (PASO)
The Pacific Aviation Safety Office (PASO) is an international organization providing quality aviation safety and security service for Member States in the Pacific.
PASO is the sole international organization responsible for regional regulatory aviation safety oversight service for the 10 Pacific States who are signatories to the Pacific Islands Civil Aviation Safety and Security Treaty (PICASST).
The current PICASST signatories are the Pacific nations of Cook Islands, Kiribati, Nauru, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu. Associate Members of PASO are Australia, Fiji and New Zealand. Government representatives from these nations make up the PASO Council.
Airspace
SkyVector – Google Maps – ADS-B Exchange
ICAO countries publish an Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP). This document is divided into three parts: General (GEN), En Route (ENR) and Aerodromes (AD). ENR 1.4 details the types of airspace classes they chose to adopt from classes A through G.
Fijian Airspace (requires user name and password).
Drone Regulations
RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aircraft System)
What is recreational use of drones?
RPAS Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a licence to fly a RPAS?
What if I want to fly my RPAS in controlled airspace?
Are there regulations for commercial RPAS flying in Fiji?
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) Regulations & Policies
None found by the author.
However, should you, the reader, happen to stumble across something to the contrary, please email the author at FISHE5CA@erau.edu and you may be mentioned in the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS section of this book by way of thanks for contributing to this free eBook!
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) News
2024 – Fiji Airways to explore cargo service with Odys VTOL aircraft
Short Essay Questions
Scenario-Based Question
You have been hired by a Drone Startup Company. Your boss has immediately assigned this job to you.
They need you to prepare a one-page memo detailing the legalities of using a drone at the beach on Kuata, pictured above.
They need you to mention any national laws and local ordinances.
They specifically want to know what airspace (insert pictures) you will be operating in and whether or not you need an airspace authorization.
Does it matter whether or not you are a citizen of the country?
Lastly, there is a bonus for you if, as you scroll through this chapter, you find any typos or broken links!
Short Essay Questions
- What are the drone categories?
- How is registration addressed?
- How is remote ID addressed?
- What are the model aircraft rules?
- What are the commercial drone rules?
- Are there waivers or exemptions to the rules? If so, for what?
- Would you share a link to an interactive airspace map?
- How is BVLOS addressed?
- How can you fly drones at night?
- How can you fly drones over people?
- Where do you find drone NOTAMs?
- What are the rules for drone maintenance?
- What are the rules for an SMS program?
- What are some unique rules not mentioned above?
- What are the C-UAS rules?
- What are the AAM rules?

